Electroluminescence
Electroluminescence is the phenomenon behind the glowing of my kitchen light. It is a process in which a material emits light when an electric current is passed through it. This occurs due to the conversion of electrical energy into light energy, making it an essential aspect of modern lighting technology. The word "electroluminescence" is derived from the Greek words "electron" and "luminescence," meaning "light produced by electricity."
Fluorescence
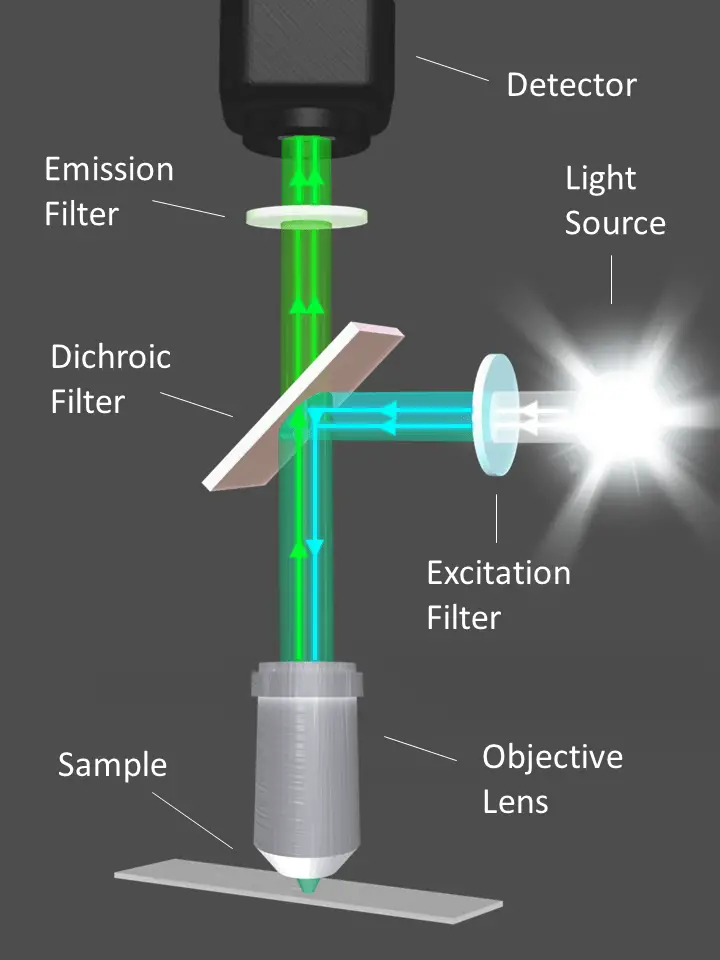
Fluorescence is a specific type of electroluminescence that occurs when a material absorbs energy from a light source and then re-emits it in the form of light. This process is commonly seen in fluorescent lights, where electricity is used to excite a gas or mercury vapor, causing it to emit UV light. This UV light is then converted into visible light by a phosphor coating inside the bulb, resulting in the characteristic glowing of fluorescent lights.
Phosphorescence
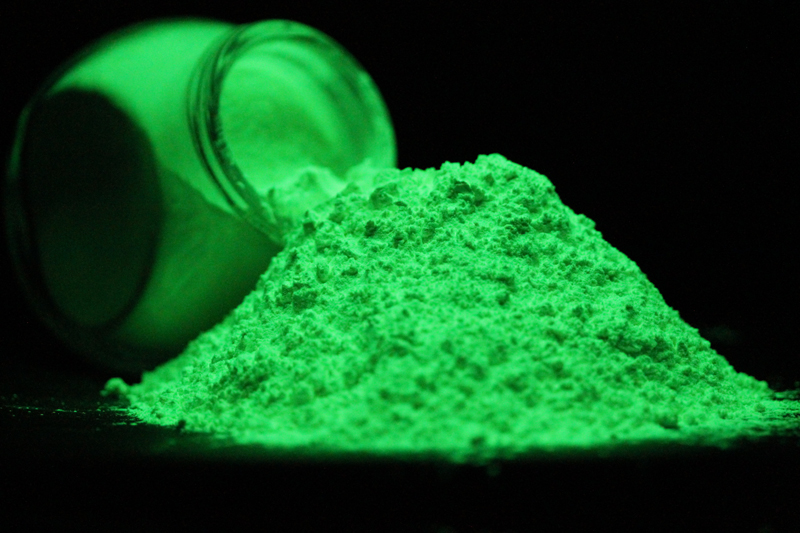
Phosphorescence is another type of electroluminescence that is similar to fluorescence but differs in the length of time the material emits light. Unlike fluorescence, which stops emitting light as soon as the energy source is removed, phosphorescent materials continue to emit light for a period of time after the energy source is removed. This is why glow-in-the-dark materials, such as toys or stickers, continue to emit light even after being exposed to light for a short period.
Incandescence
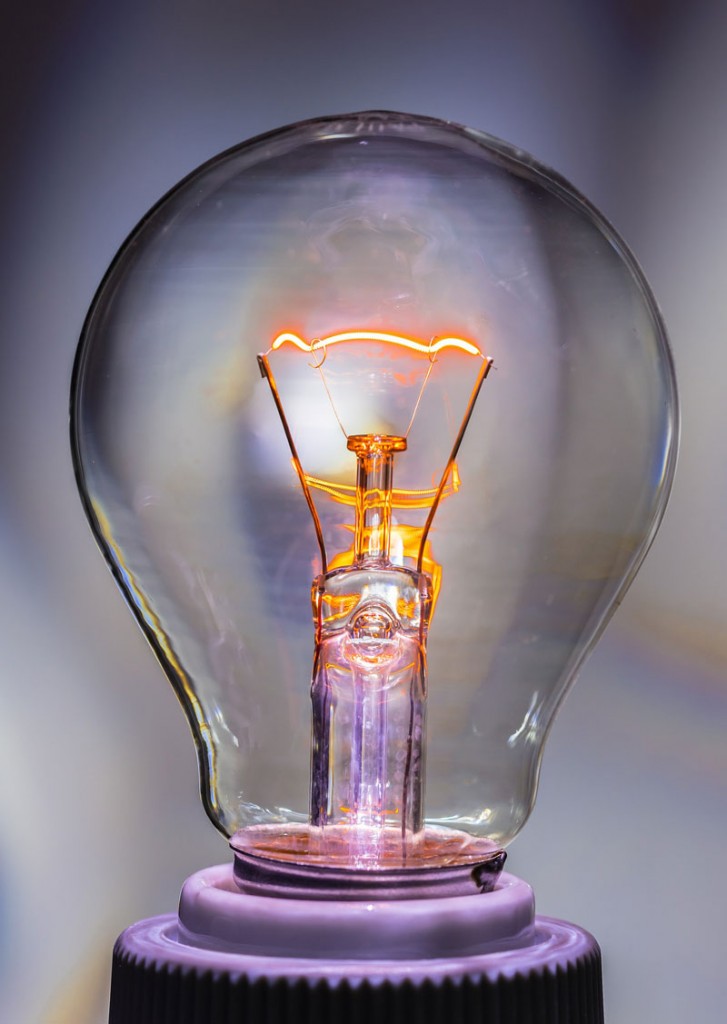
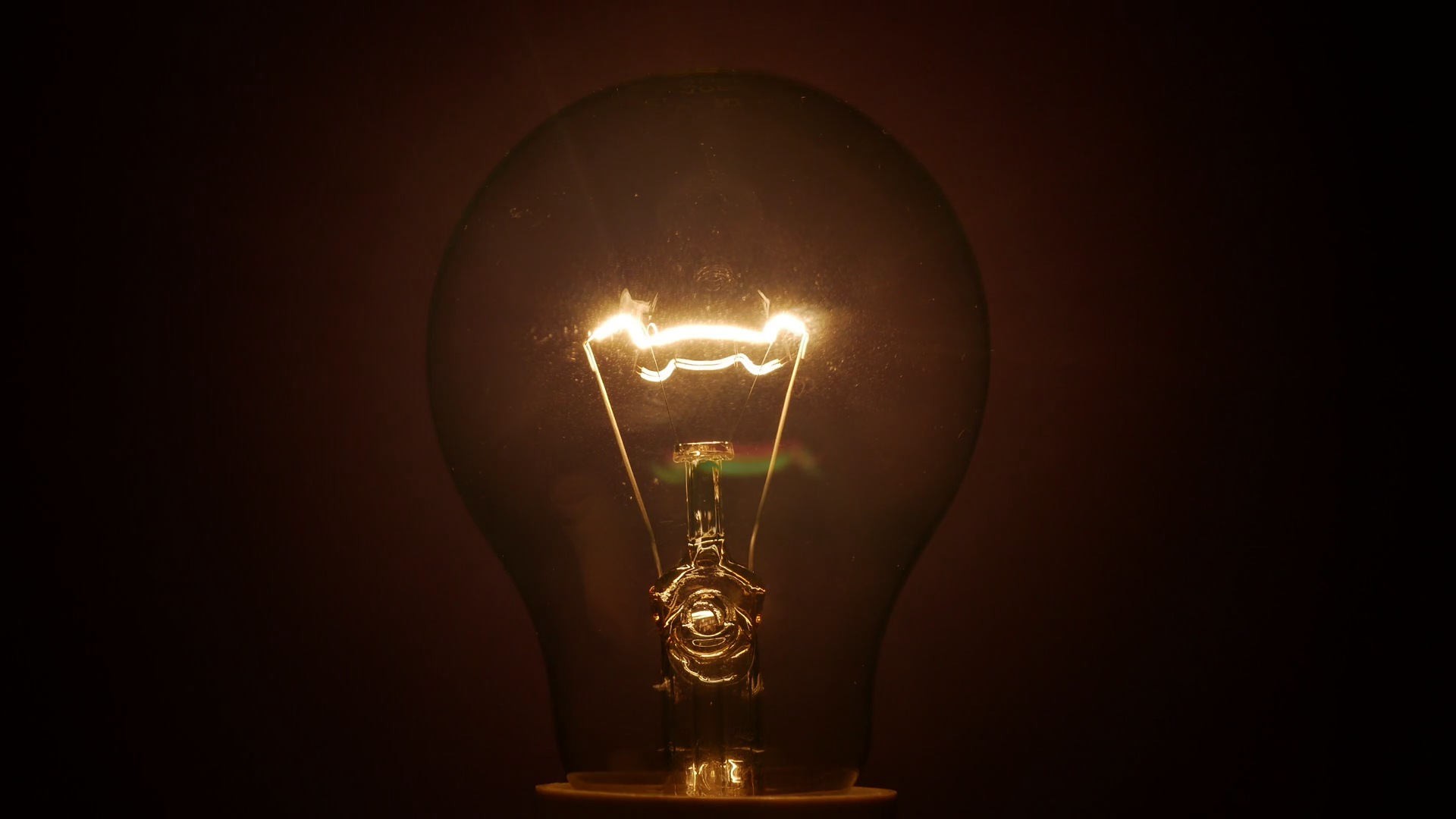
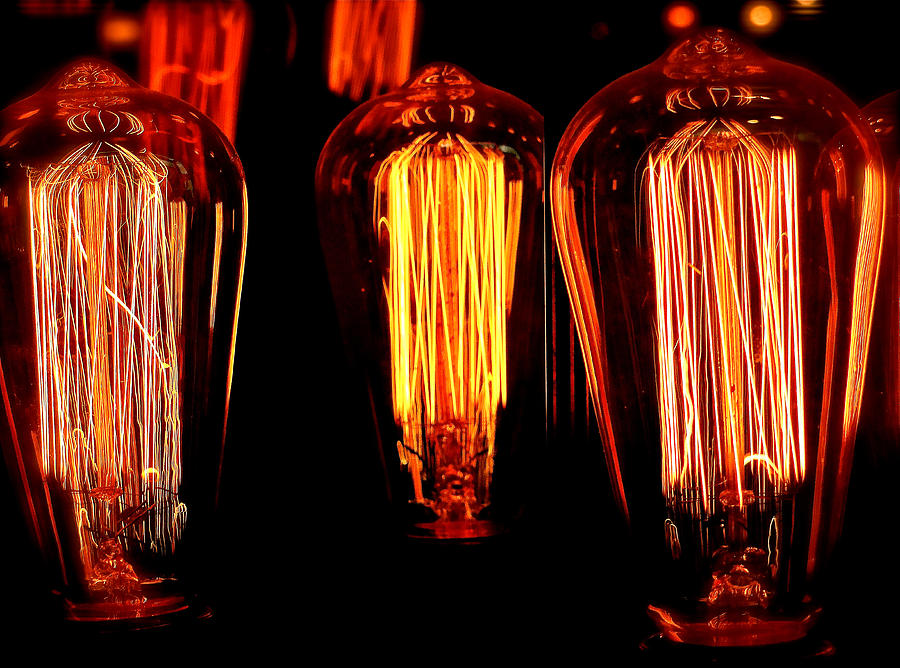
Incandescence is a type of thermal radiation that occurs when an object is heated to a high temperature, causing it to emit visible light. This process is commonly seen in traditional incandescent light bulbs, where electricity is used to heat a thin wire filament to a high temperature, causing it to emit light. However, incandescent bulbs are not very energy-efficient and have been largely replaced by other types of electroluminescent lighting technology.
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
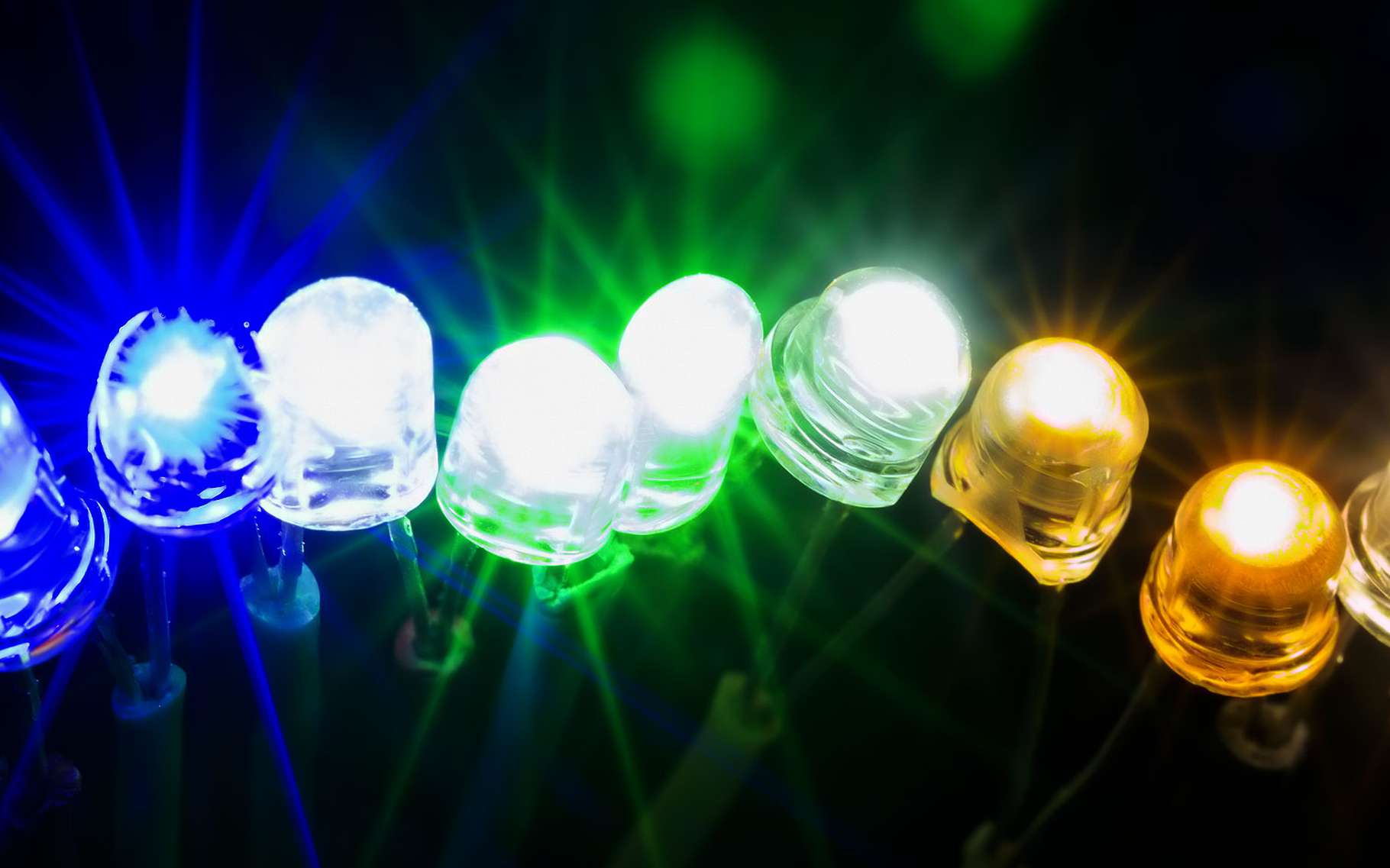
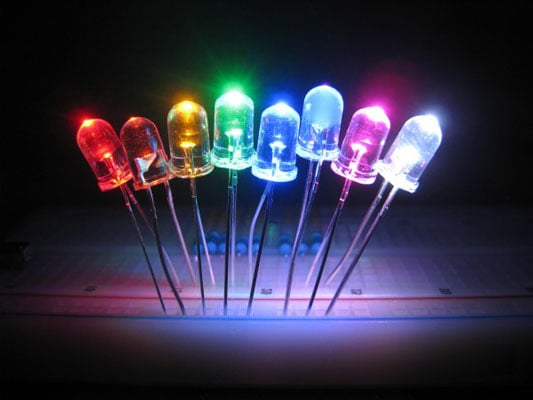
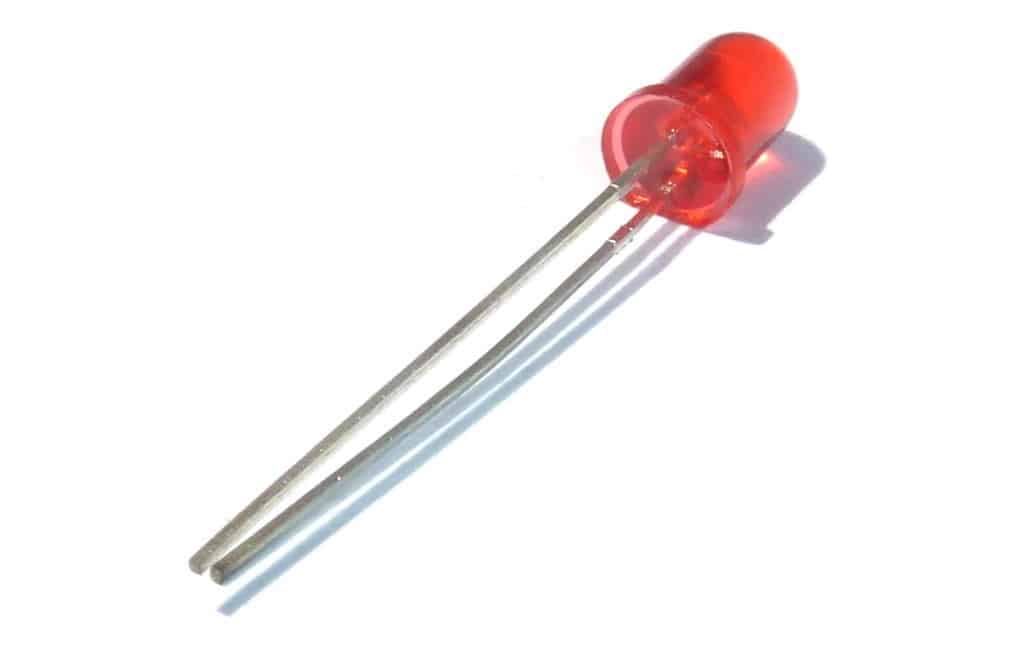
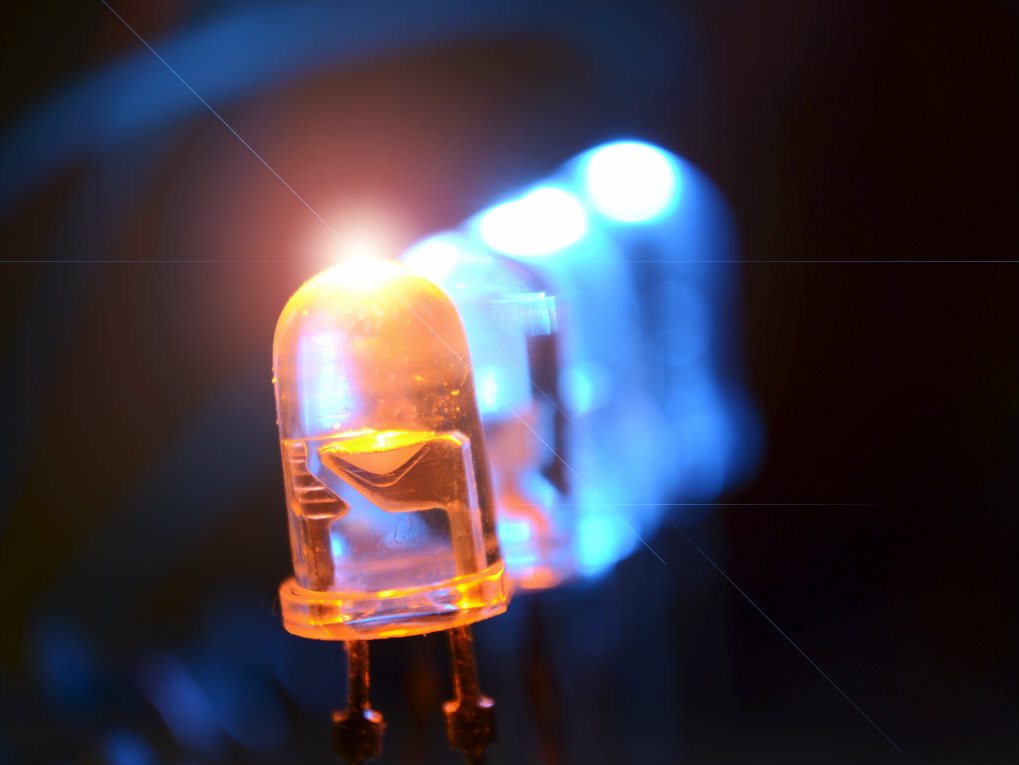
Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) are a type of semiconductor device that emits light when a current passes through it. Unlike incandescent bulbs, which emit light by heating a filament, LEDs emit light through a process called electroluminescence. This process involves the movement of electrons through a semiconductor material, causing them to release energy in the form of light. LEDs are highly energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan compared to incandescent bulbs, making them a popular choice for modern lighting solutions.
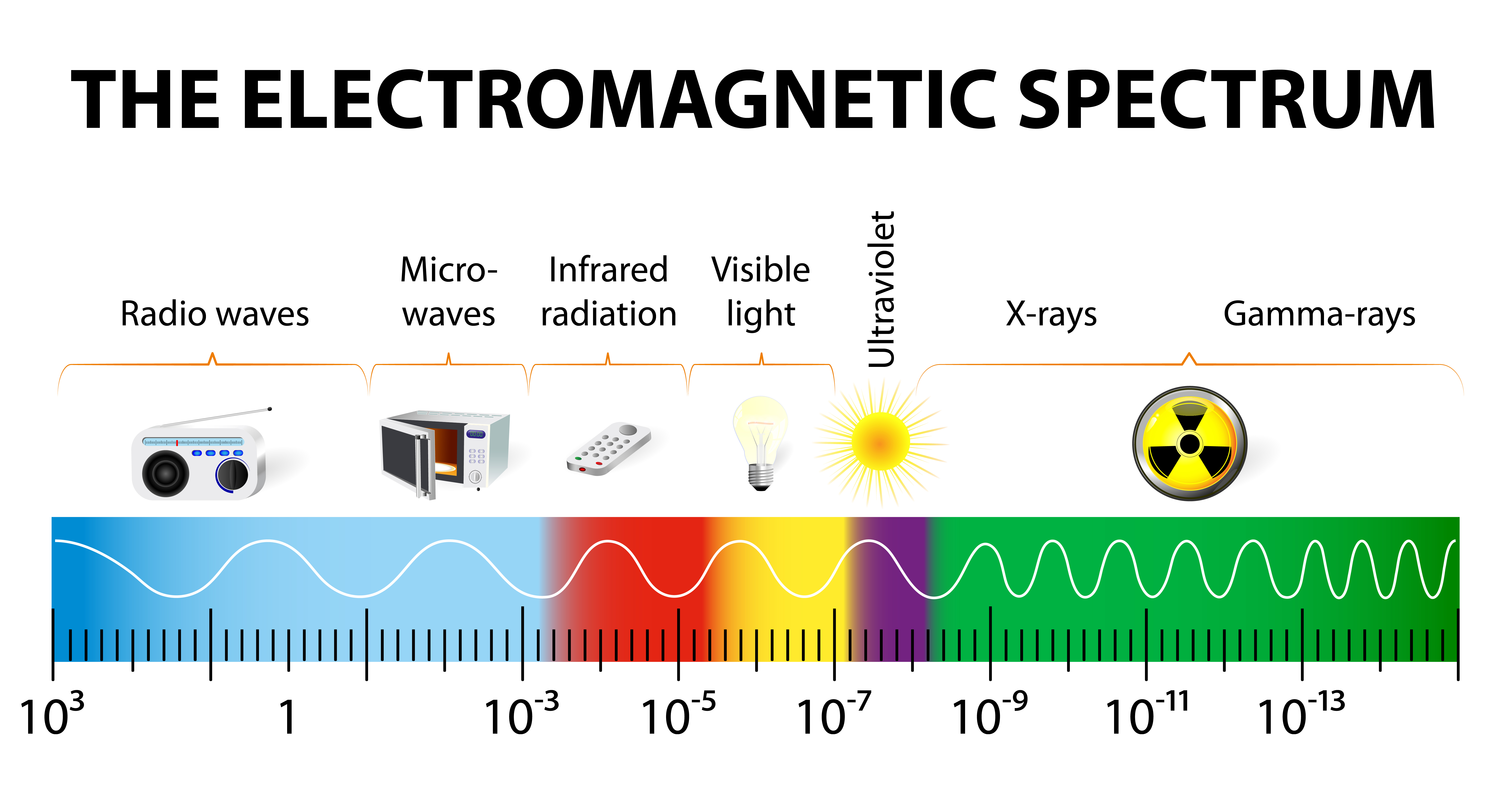
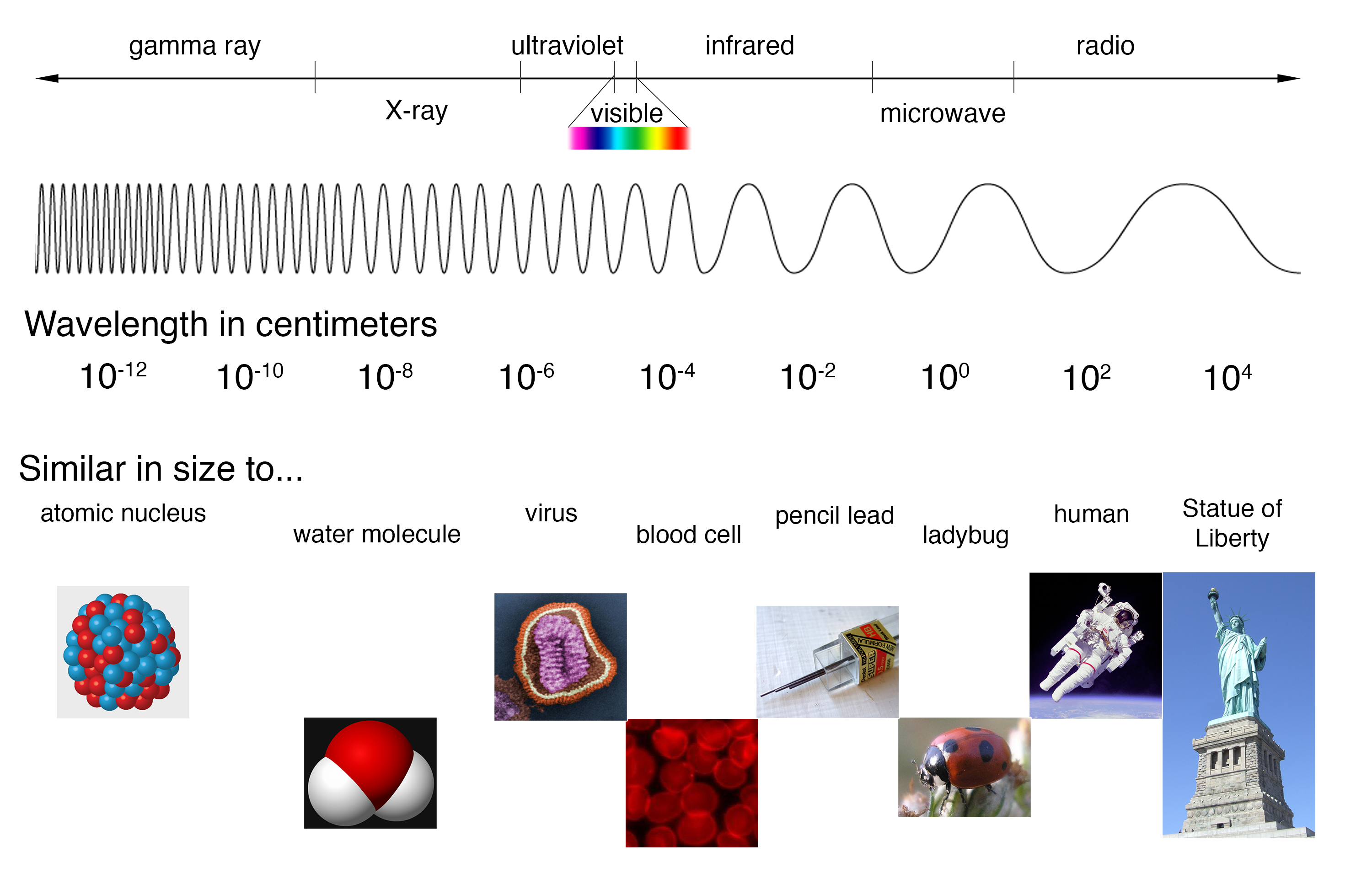
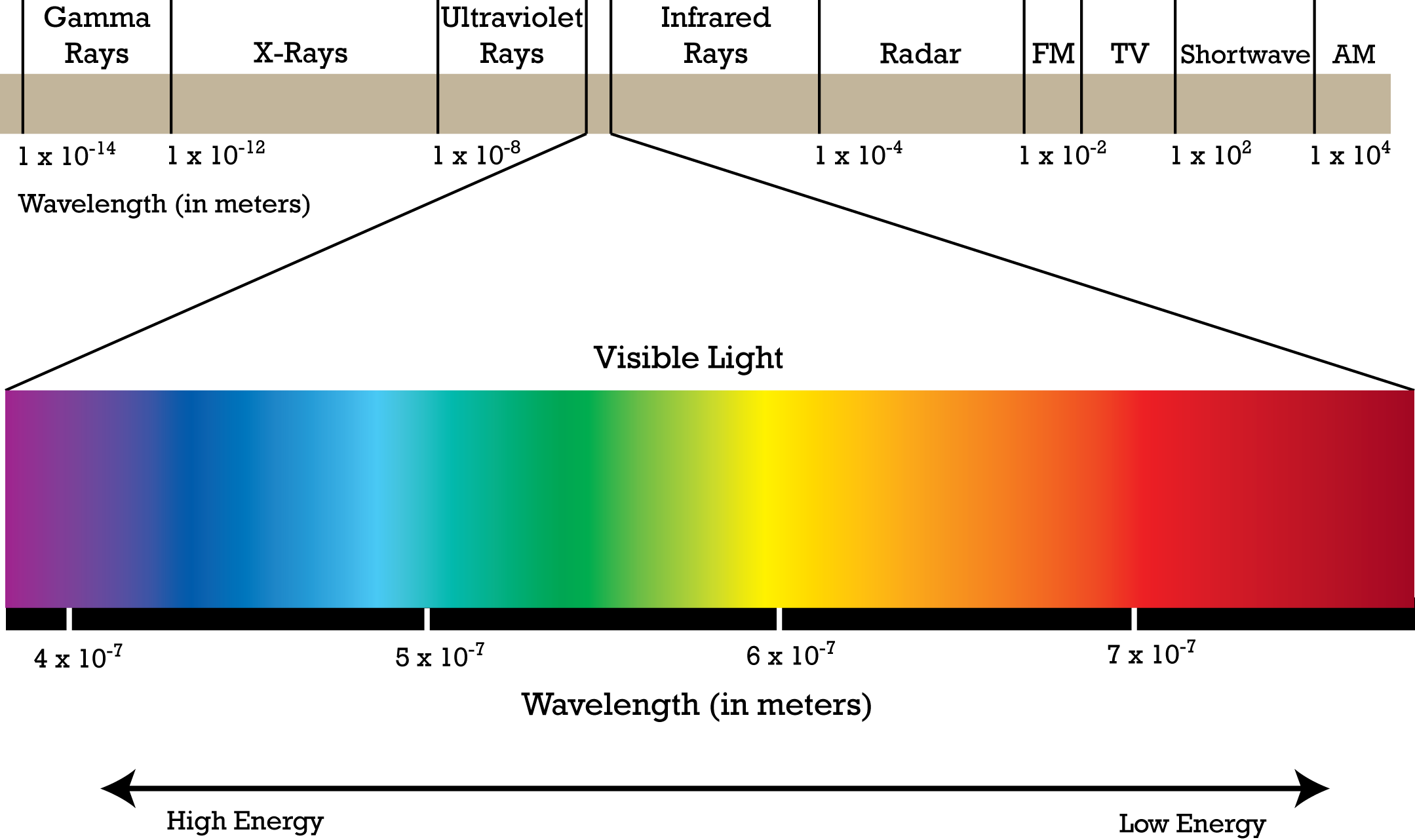
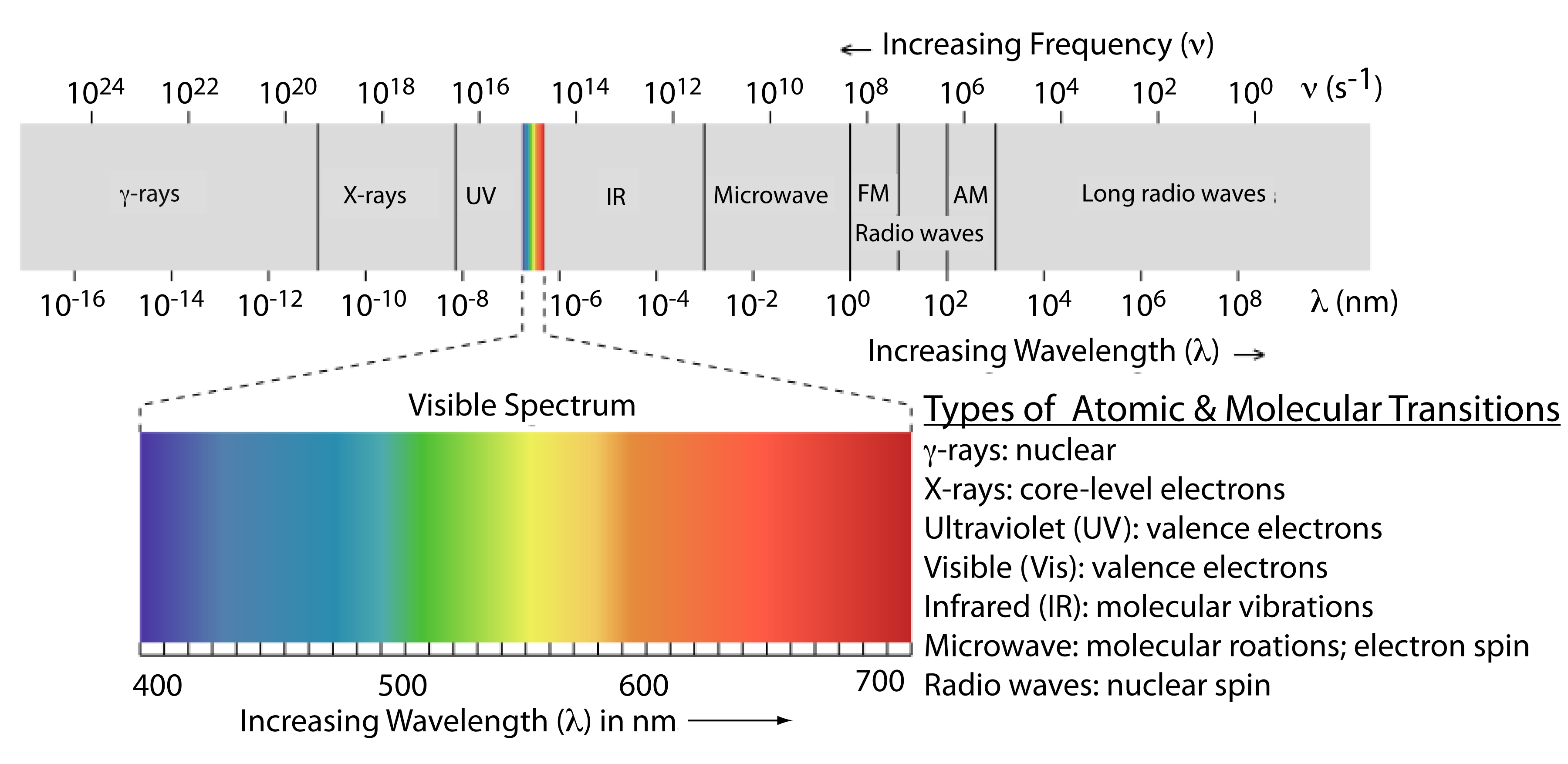
Electromagnetic Spectrum
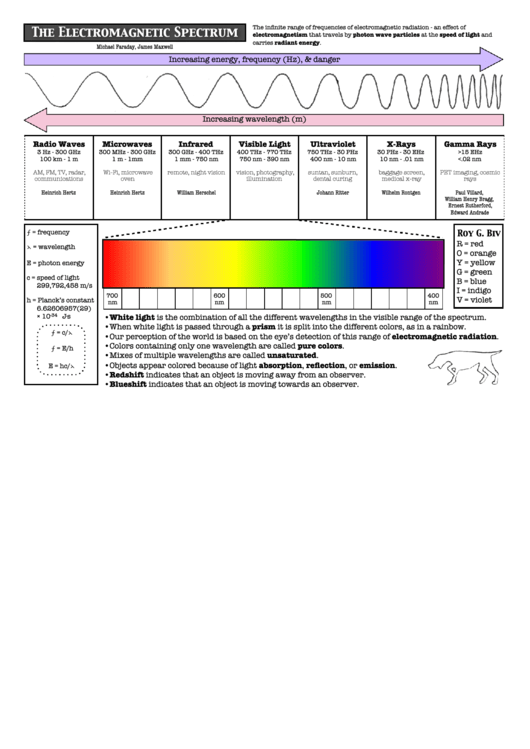
Electromagnetic Spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. This includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. The different types of electroluminescence, such as fluorescence and incandescence, are all part of the electromagnetic spectrum, with each type of light having a different frequency and wavelength.
Energy Conversion
Energy Conversion is a crucial concept in understanding the science behind my kitchen light glowing. As mentioned earlier, electroluminescence involves the conversion of electrical energy into light energy, making it an essential process in modern lighting technology. This process is also seen in other forms of lighting, such as solar panels, where sunlight is converted into electricity.
Quantum Mechanics
Quantum Mechanics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior of matter and energy at a microscopic level. It is a fundamental theory that helps explain the science behind electroluminescence. According to quantum mechanics, atoms and molecules have discrete energy levels, and when they absorb energy, they jump to a higher energy level. When they return to their original energy level, they release energy in the form of light, resulting in electroluminescence.
Electricity
Electricity is the flow of electric charge through a conductor, such as a wire. This flow of electric charge is what powers our kitchen light and causes it to glow. The electricity travels through the wires in our house, and when it reaches the light bulb, it passes through a filament or semiconductor material, causing it to emit light through the process of electroluminescence.
Chemiluminescence
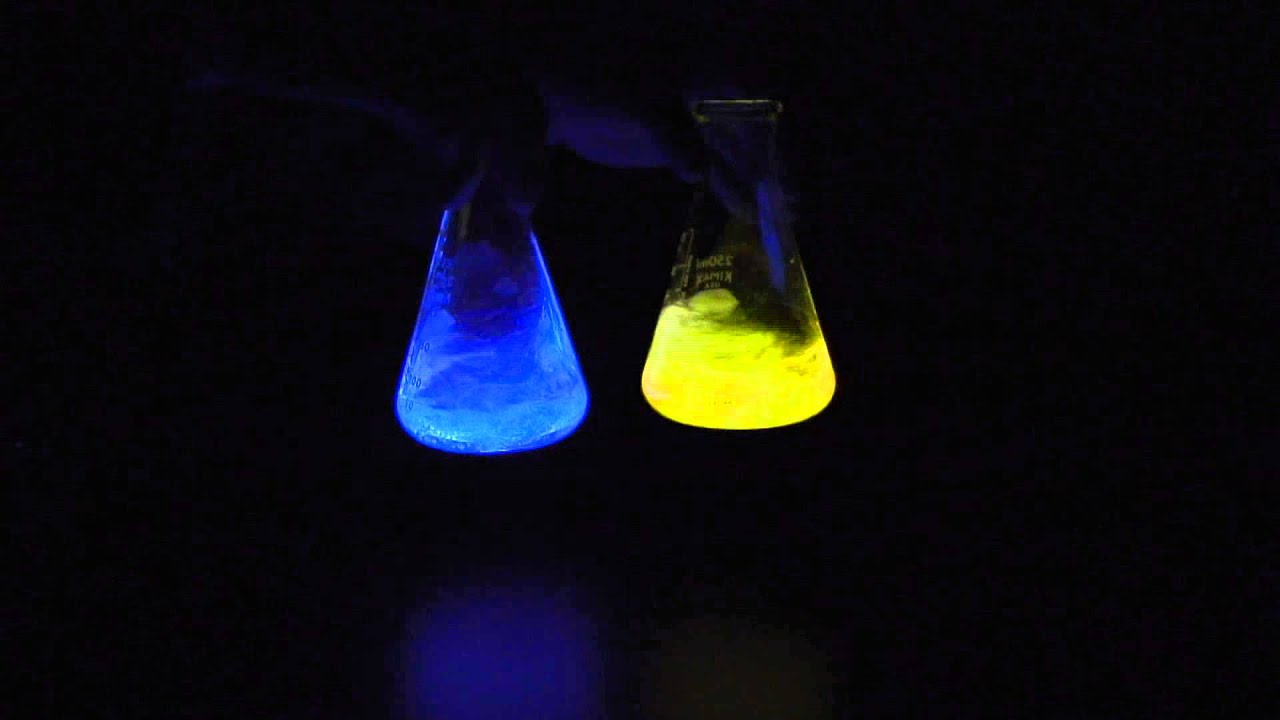
Chemiluminescence is a type of electroluminescence that occurs due to a chemical reaction instead of an electric current. This process involves the conversion of chemical energy into light energy, resulting in a glow. It is commonly seen in glow sticks, where two chemicals are mixed to produce light. However, unlike other forms of electroluminescence, chemiluminescence does not require an external energy source to produce light.
The Science Behind My Kitchen Light Glowing

Understanding Light and Electricity
 When we flip a switch and turn on a light in our kitchen, it may seem like a simple and mundane action. However, there is actually a complex scientific process happening behind the scenes. To understand the science behind your kitchen light glowing, we first need to understand the properties of light and electricity.
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It travels in waves and is made up of particles called photons. When light hits an object, some of the photons are absorbed while others are reflected. This is what allows us to see objects and colors in our environment.
Electricity, on the other hand, is a flow of electrons through a conductor. In order for electricity to flow and create light, there needs to be a complete circuit, with a source of energy, such as a power plant, and a pathway for the electricity to travel, such as wires.
When we flip a switch and turn on a light in our kitchen, it may seem like a simple and mundane action. However, there is actually a complex scientific process happening behind the scenes. To understand the science behind your kitchen light glowing, we first need to understand the properties of light and electricity.
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye. It travels in waves and is made up of particles called photons. When light hits an object, some of the photons are absorbed while others are reflected. This is what allows us to see objects and colors in our environment.
Electricity, on the other hand, is a flow of electrons through a conductor. In order for electricity to flow and create light, there needs to be a complete circuit, with a source of energy, such as a power plant, and a pathway for the electricity to travel, such as wires.
The Role of Incandescent Bulbs
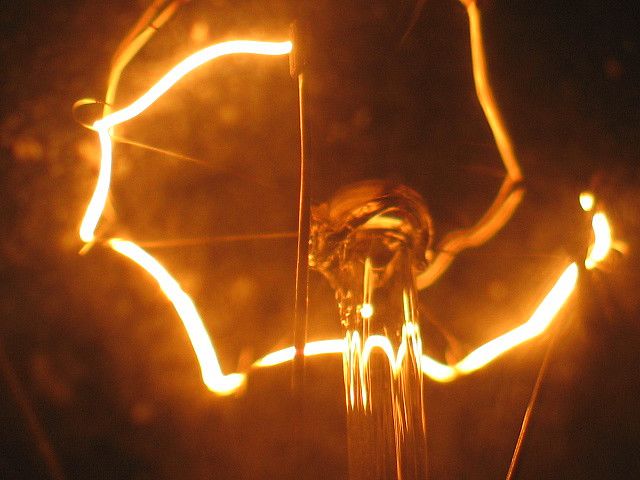
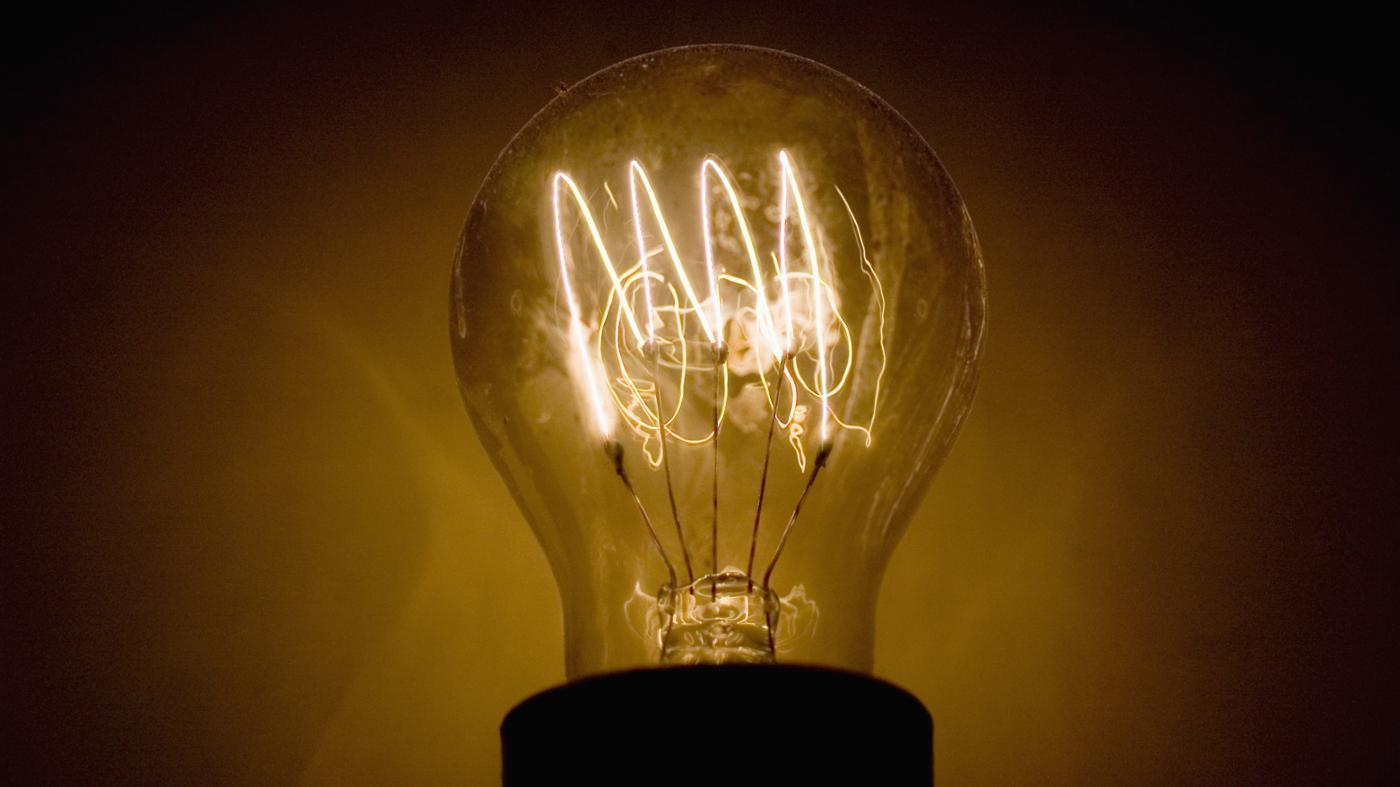
 The most common type of light bulb found in most homes is the incandescent bulb. These bulbs work by passing electricity through a thin filament inside the bulb, causing it to heat up and produce light. The filament is typically made of a tungsten wire, which has a high melting point and can withstand the high temperatures needed to produce light.
Fun fact:
The filament in an incandescent bulb can reach temperatures of up to 4,600 degrees Fahrenheit, which is why they can be a fire hazard if not used properly.
When electricity flows through the filament, it causes it to glow and emit light. The amount of light produced is determined by the amount of electricity flowing through the filament. This is why you can adjust the brightness of a light by using a dimmer switch, which controls the amount of electricity flowing through the circuit.
The most common type of light bulb found in most homes is the incandescent bulb. These bulbs work by passing electricity through a thin filament inside the bulb, causing it to heat up and produce light. The filament is typically made of a tungsten wire, which has a high melting point and can withstand the high temperatures needed to produce light.
Fun fact:
The filament in an incandescent bulb can reach temperatures of up to 4,600 degrees Fahrenheit, which is why they can be a fire hazard if not used properly.
When electricity flows through the filament, it causes it to glow and emit light. The amount of light produced is determined by the amount of electricity flowing through the filament. This is why you can adjust the brightness of a light by using a dimmer switch, which controls the amount of electricity flowing through the circuit.
The Importance of Wiring and Voltage
 Now that we understand the basics of light and electricity, we can delve into the specifics of how your kitchen light glows. The wiring in your home plays a crucial role in delivering the electricity needed to power your light bulb. The wiring needs to be properly connected and insulated to ensure that the electricity flows smoothly and safely.
Additionally, the voltage of the electricity also plays a part in the glow of your kitchen light. Voltage is the force or pressure that pushes electricity through the circuit. Most homes in the United States have a voltage of 120 volts, which is enough to power the average incandescent light bulb. However, if the voltage is too high, it can cause the filament to overheat and burn out quickly.
In conclusion, the science behind your kitchen light glowing involves a combination of light and electricity. By understanding the properties of these two elements and how they work together, we can better appreciate the simple act of flipping a switch and illuminating our kitchen. So next time you turn on your kitchen light, remember the complex process that is happening behind the scenes.
Now that we understand the basics of light and electricity, we can delve into the specifics of how your kitchen light glows. The wiring in your home plays a crucial role in delivering the electricity needed to power your light bulb. The wiring needs to be properly connected and insulated to ensure that the electricity flows smoothly and safely.
Additionally, the voltage of the electricity also plays a part in the glow of your kitchen light. Voltage is the force or pressure that pushes electricity through the circuit. Most homes in the United States have a voltage of 120 volts, which is enough to power the average incandescent light bulb. However, if the voltage is too high, it can cause the filament to overheat and burn out quickly.
In conclusion, the science behind your kitchen light glowing involves a combination of light and electricity. By understanding the properties of these two elements and how they work together, we can better appreciate the simple act of flipping a switch and illuminating our kitchen. So next time you turn on your kitchen light, remember the complex process that is happening behind the scenes.
















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/colorful-liquid-in-motion-146967876-578a68763df78c09e9e3f65a.jpg)










/colorful-liquid-in-motion-146967876-578a68763df78c09e9e3f65a.jpg)
























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/electromagnetic-spectrum--the-visible-range--shaded-portion--is-shown-enlarged-on-the-right--141483219-59886cfa0d327a00113aafb6.jpg)
































/flasks-with-glowing-liquids-520120820-594044535f9b58d58a548082.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/glowsticks-182836423-59418d8b5f9b58d58ac12fd4.jpg)












