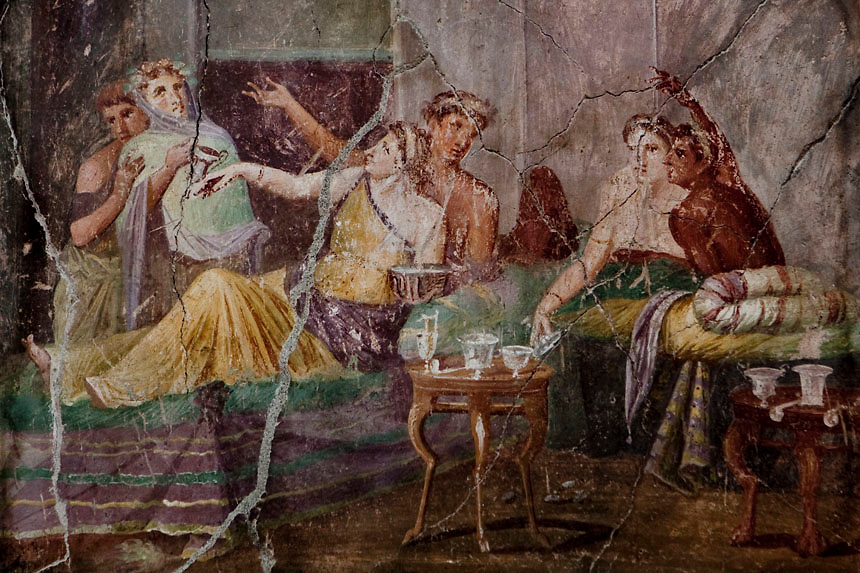Introduction
Dining was an integral part of ancient Roman culture, and it was considered a symbol of wealth, power, and social status. The ancient Romans took great pride in their dining rooms, also known as tricliniums, and they were often the center of social gatherings and lavish banquets. Let's take a closer look at the top 10 dining rooms in ancient Rome and discover the fascinating customs, rituals, and practices associated with feasting in this ancient civilization.
1. Ancient Roman Dining Rooms
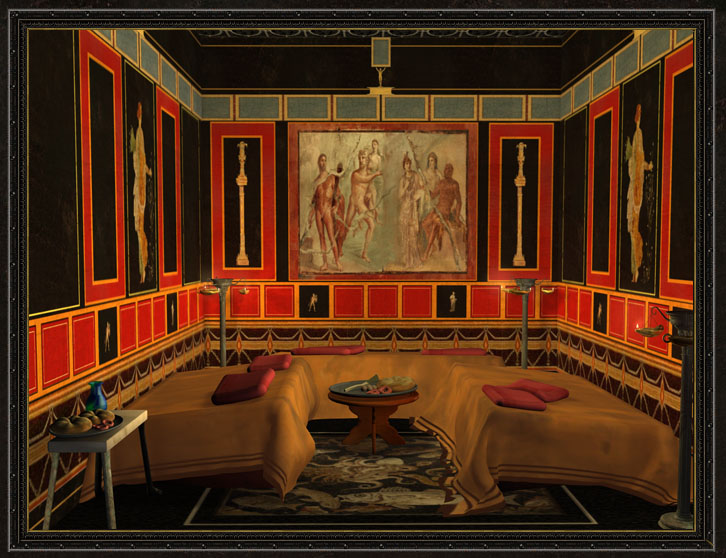
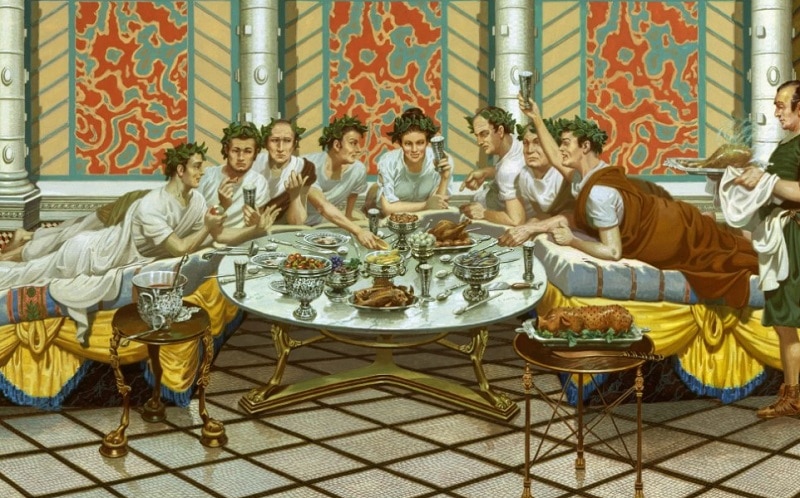
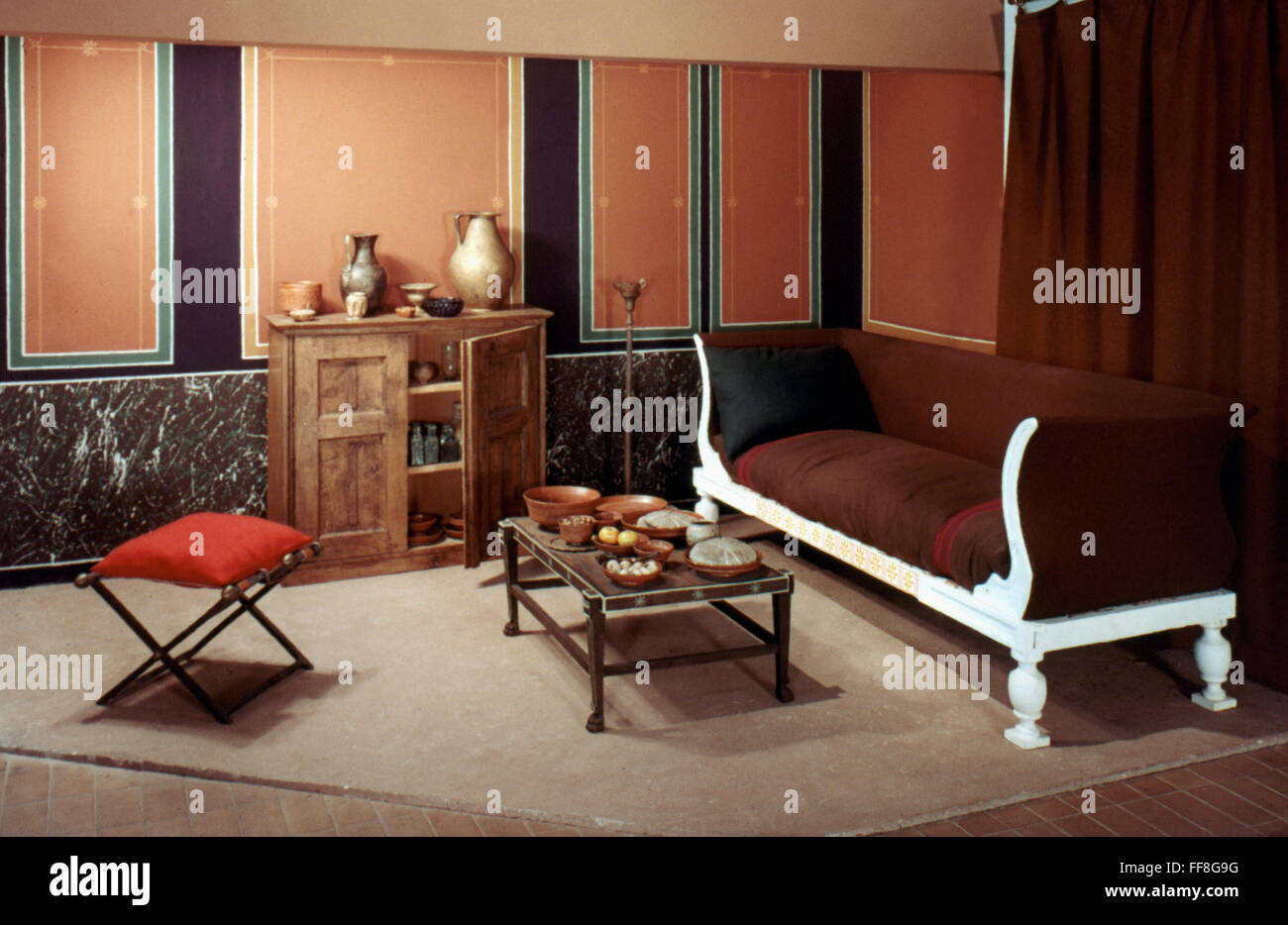
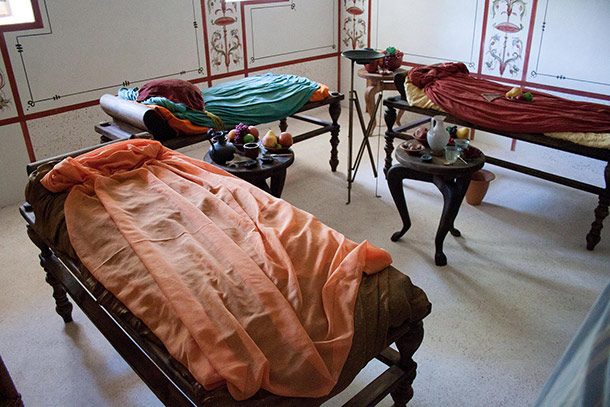
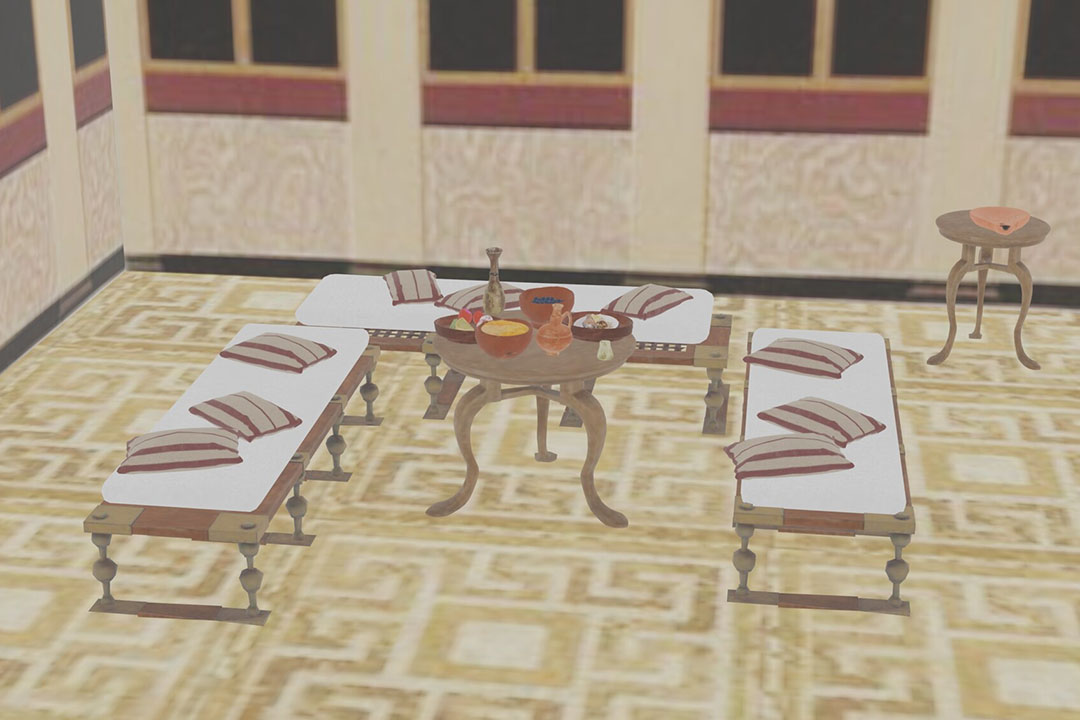
The ancient Romans had a dedicated room for dining, known as a triclinium, which means "three couches" in Latin. These rooms were typically rectangular in shape and were adorned with intricate frescoes, mosaics, and sculptures. The dining room was often located on the ground floor of a Roman villa, and it was considered the heart of the household.
2. Roman Banquet Halls
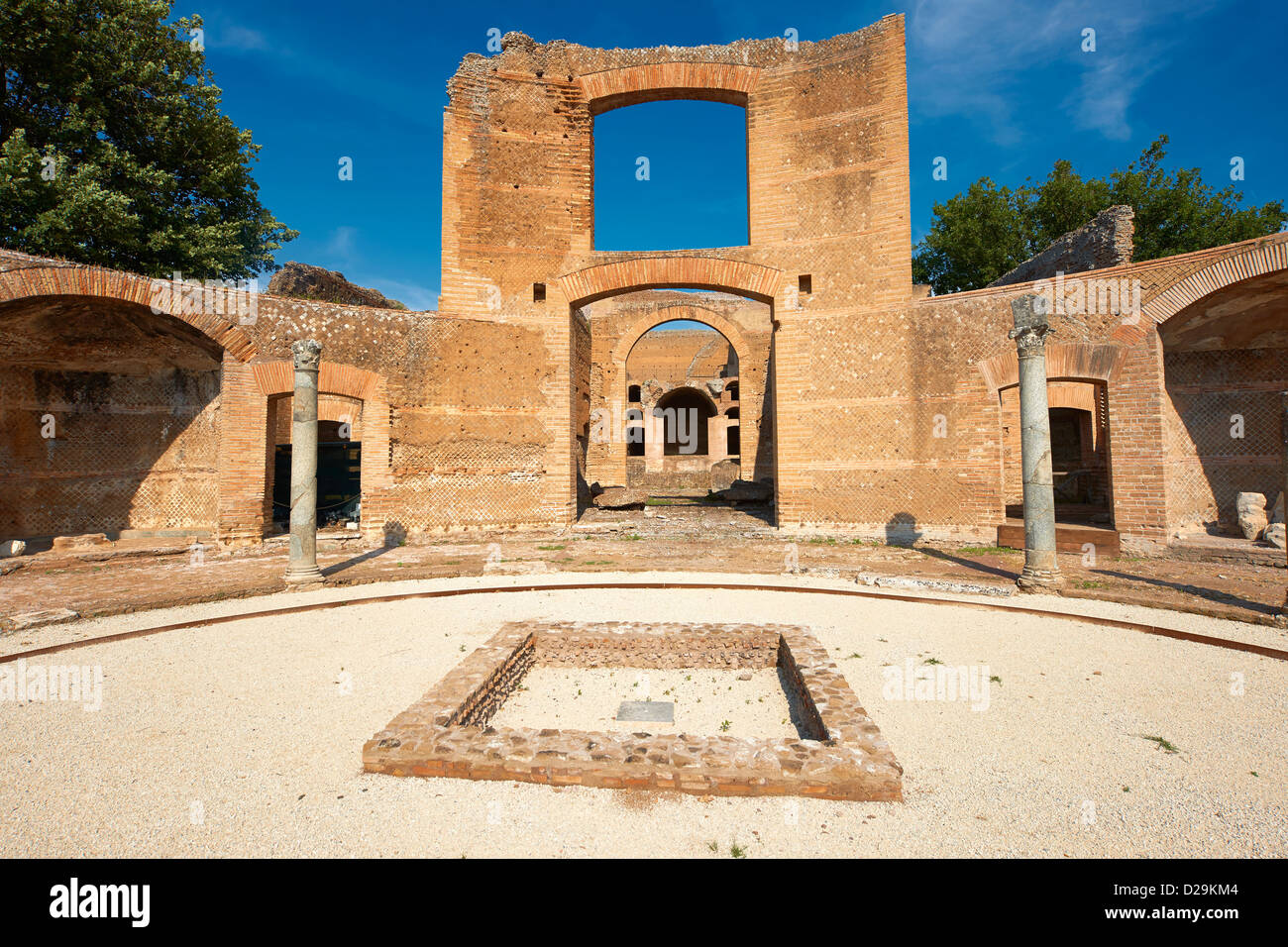
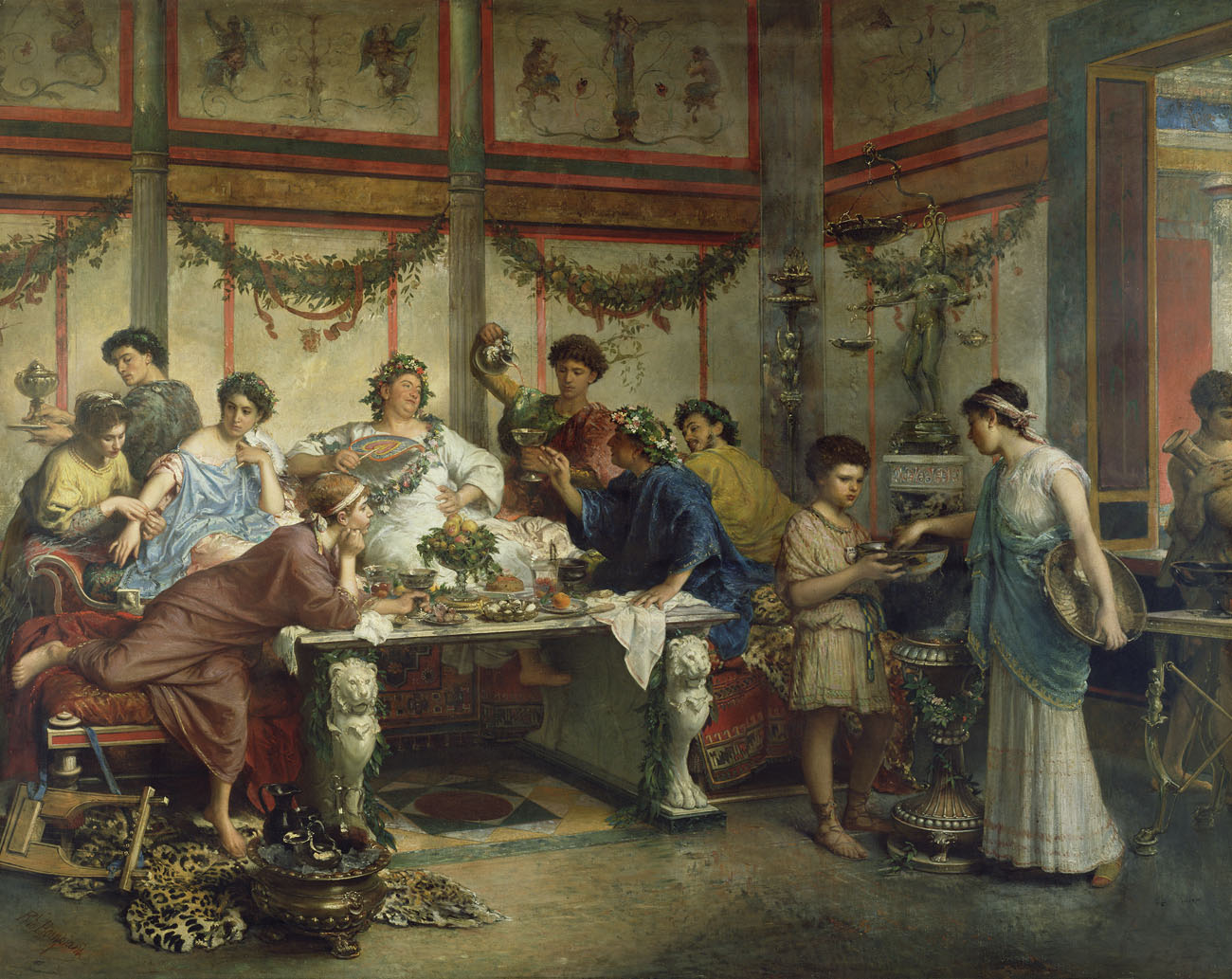
In addition to private dining rooms, the ancient Romans also had large banquet halls, known as coenacula. These halls were used for hosting grand feasts and celebrations, and they were often decorated with extravagant furnishings and elaborate feasting tables. The most famous coenacula in ancient Rome was the Triclinium Leoninum, located in the Lateran Palace.
3. Triclinium
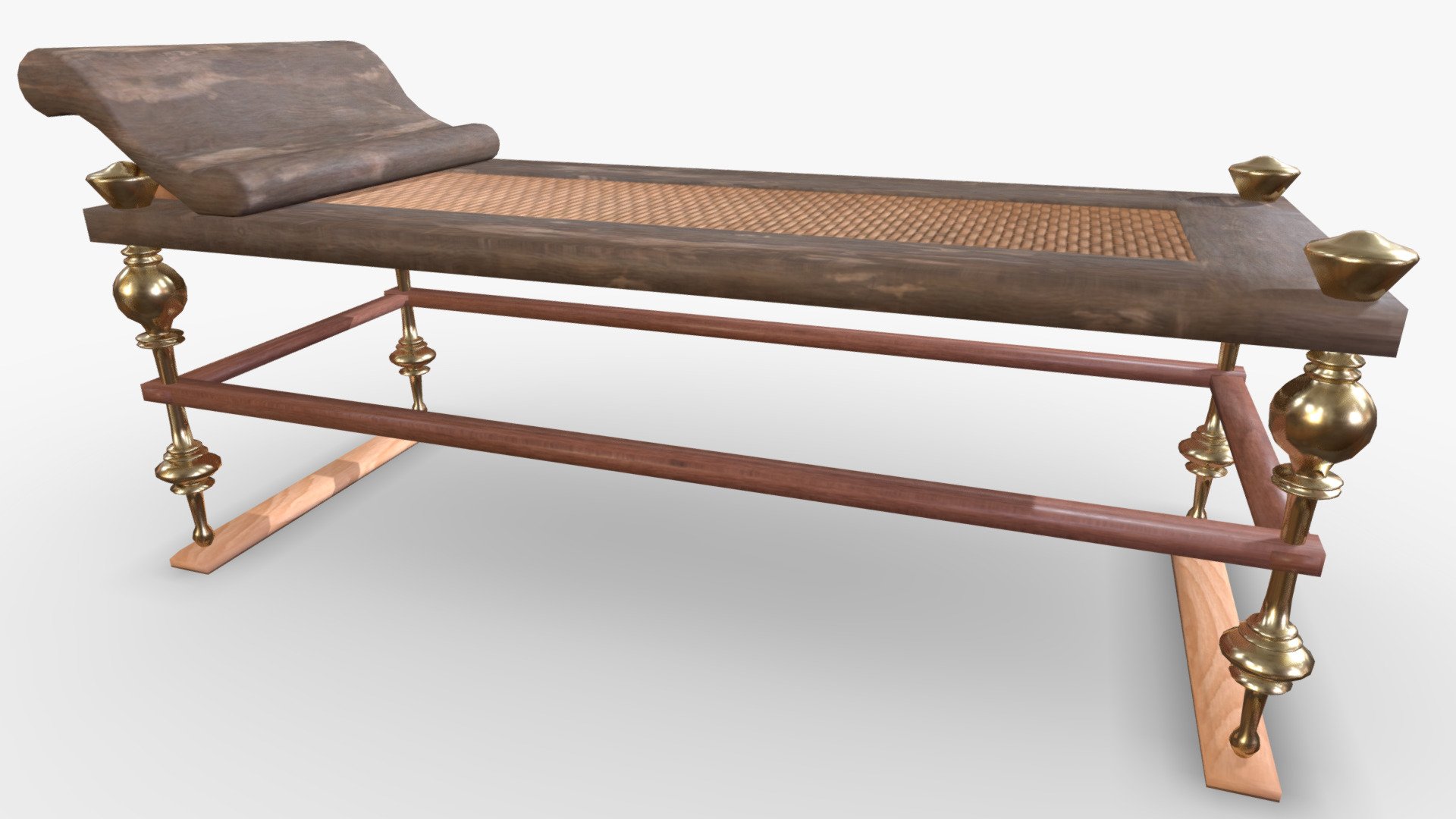
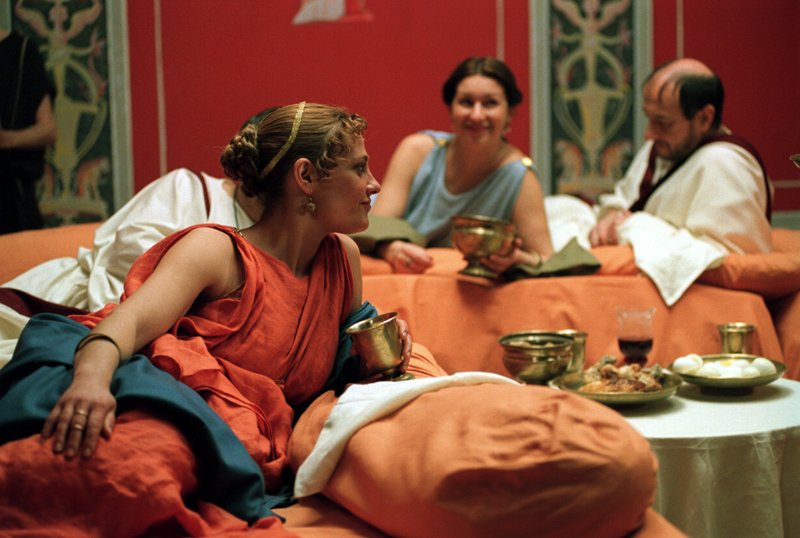
The triclinium was the main dining area in a Roman villa, and it was where the family and their guests would gather to eat their meals. The room was typically divided into three sections, each containing a dining couch, known as a lectus. The lectus was a low, cushioned couch where guests would recline while dining.
4. Ancient Roman Feasting
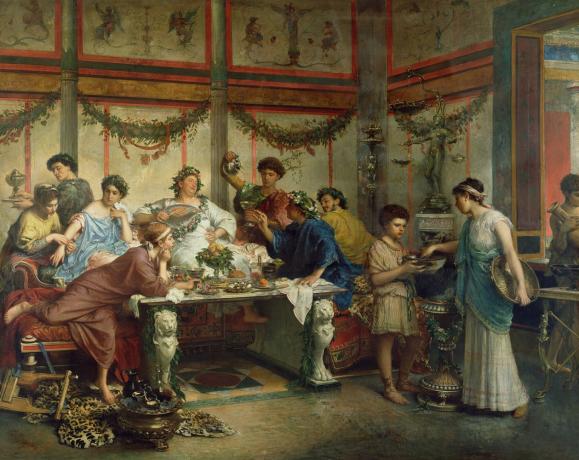
Feasting was a common practice in ancient Rome, and it was an important way for the wealthy to display their wealth and social status. These feasts were grand affairs that could last for hours, and they were often accompanied by entertainment, such as music, dancing, and performances. The most lavish feasts were reserved for special occasions, such as weddings, birthdays, and religious festivals.
5. Roman Dining Customs
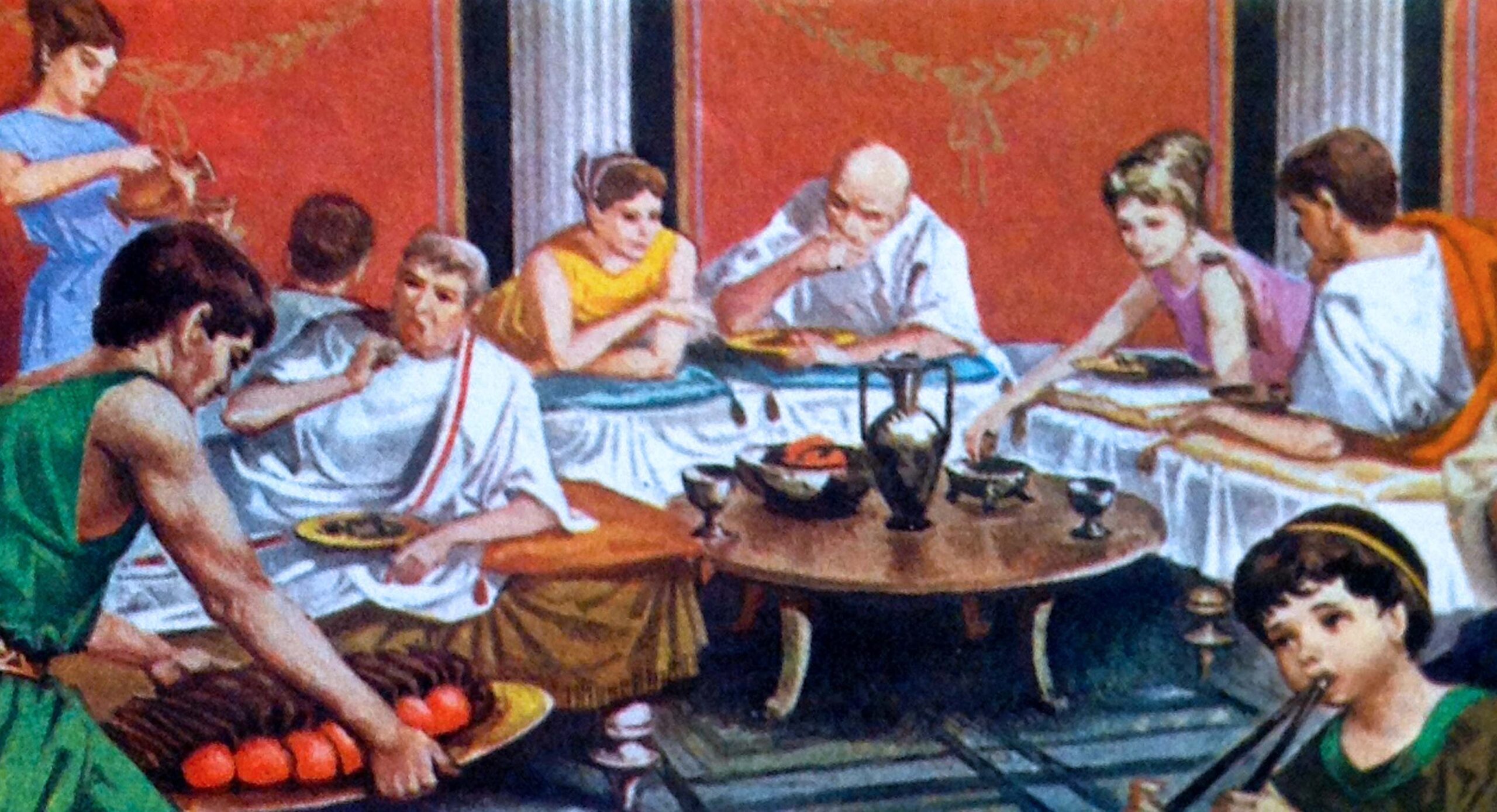
The ancient Romans had a strict set of dining customs and etiquette that were followed during meals. For example, it was customary for guests to wash their hands before dining, and they would often use a small towel known as a mappa to wipe their hands during the meal. It was also common for guests to bring their own napkins, which would be used to wrap any leftover food to take home.
6. Ancient Roman Culinary Culture
Food was an essential part of ancient Roman culture, and they were known for their diverse and flavorful cuisine. The Romans were skilled at using a variety of ingredients, including meats, fish, vegetables, and spices, to create delicious and elaborate dishes. Some of the most popular dishes included roasted meats, stews, and pastries.
7. Roman Dining Etiquette
The ancient Romans had strict rules when it came to dining etiquette. For example, it was considered impolite to chew with your mouth open or talk while eating. Guests were also expected to pace themselves and not eat too quickly or too slowly. It was also customary for hosts to offer their guests a variety of foods and drinks, and it was considered rude to refuse.
8. Ancient Roman Dining Furniture
The ancient Romans had a variety of dining furniture, including tables, chairs, and couches. The most common type of dining table was the mensa, which was a low, rectangular table used for feasting. The Romans also had a variety of dining chairs, including the sella, which was a simple wooden chair, and the cathedra, which was a more elaborate throne-like chair used by the host.
9. Roman Dining Rituals
In addition to strict dining etiquette, the ancient Romans also had various dining rituals and traditions. For example, before a meal, guests would often offer a libation to the gods by pouring a small amount of wine onto the floor. It was also customary for the host to offer a prayer before the meal, and guests would often sprinkle salt on their food as a symbol of friendship and loyalty.
The Significance of the Dining Room in Ancient Rome Homes

Introduction
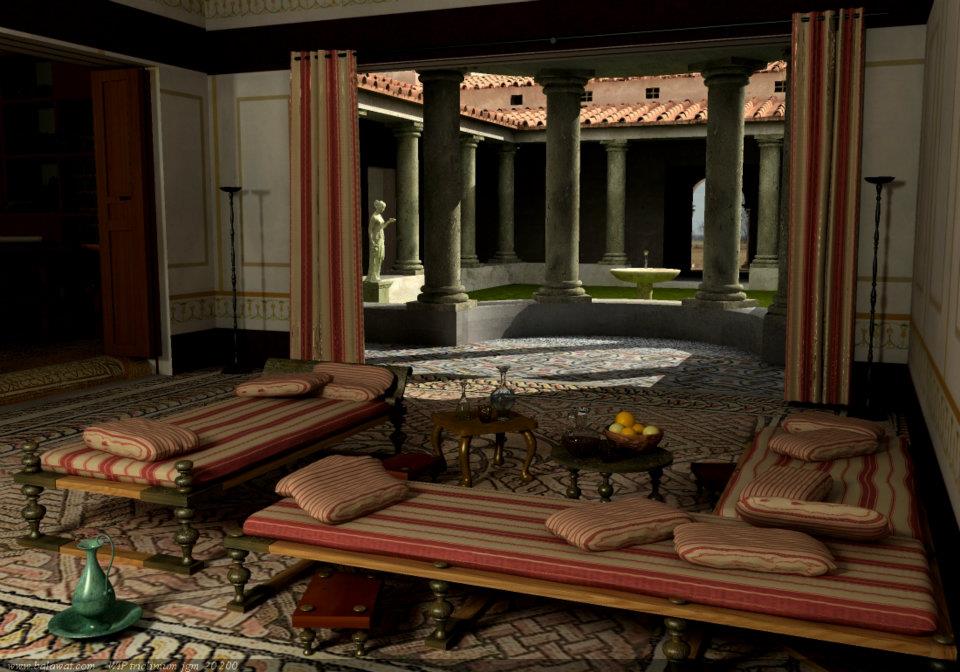 The ancient Romans were known for their grandiose and luxurious architecture, with their homes being a prime example of their wealth and lavish lifestyle. Each aspect of their homes, including the dining room, was carefully designed and decorated to showcase their status and social standing. The dining room in ancient Rome homes was not just a place to eat, but also a space for socializing and displaying their opulence. Let us delve deeper into the significance of the dining room in ancient Rome homes.
The ancient Romans were known for their grandiose and luxurious architecture, with their homes being a prime example of their wealth and lavish lifestyle. Each aspect of their homes, including the dining room, was carefully designed and decorated to showcase their status and social standing. The dining room in ancient Rome homes was not just a place to eat, but also a space for socializing and displaying their opulence. Let us delve deeper into the significance of the dining room in ancient Rome homes.
Functionality of the Dining Room
 In ancient Rome, the dining room, also known as the triclinium, was an essential part of the house.
Dining
was considered a vital social activity for the Romans, and the triclinium was where they would gather with family and friends to
enjoy
their meals. It was a multi-functional space that served as a private dining area, a reception room for guests, and a place for leisurely activities such as reading and lounging.
In ancient Rome, the dining room, also known as the triclinium, was an essential part of the house.
Dining
was considered a vital social activity for the Romans, and the triclinium was where they would gather with family and friends to
enjoy
their meals. It was a multi-functional space that served as a private dining area, a reception room for guests, and a place for leisurely activities such as reading and lounging.
Design and Decor
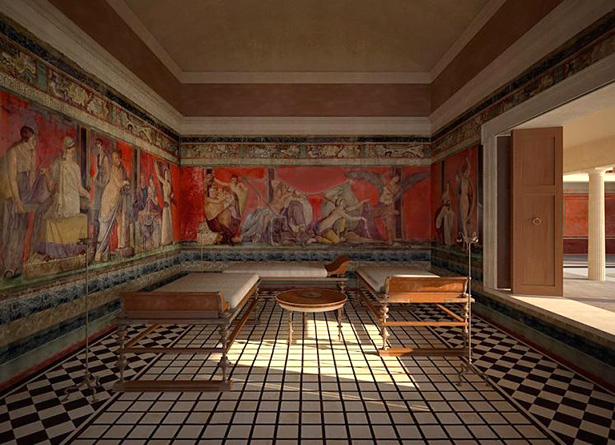
 The dining room in ancient Rome homes was designed to impress and reflect the owner's wealth and social status. The walls were adorned with
fresco
paintings, depicting scenes of lavish banquets and exotic landscapes. The floors were usually made of
mosaic
tiles, with intricate designs and patterns. The centerpiece of the dining room was the
triclinium
(dining couch), where the guests would recline while
feasting
. The triclinium was often made of
marble
and
decorated
with luxurious fabrics and
pillows
.
The dining room in ancient Rome homes was designed to impress and reflect the owner's wealth and social status. The walls were adorned with
fresco
paintings, depicting scenes of lavish banquets and exotic landscapes. The floors were usually made of
mosaic
tiles, with intricate designs and patterns. The centerpiece of the dining room was the
triclinium
(dining couch), where the guests would recline while
feasting
. The triclinium was often made of
marble
and
decorated
with luxurious fabrics and
pillows
.
Symbolism of the Dining Room
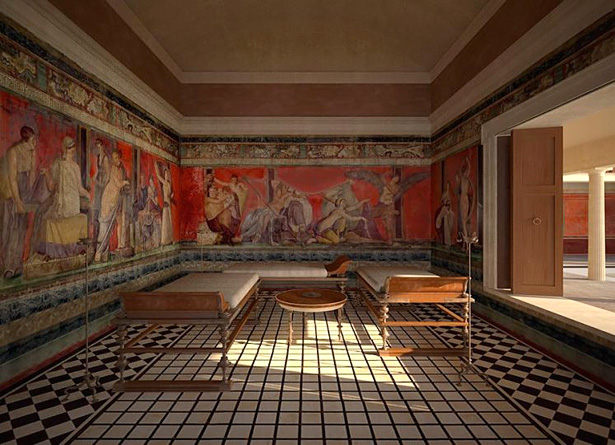 The dining room in ancient Rome homes was not just a mere functional space, but it also held symbolic significance. It was a representation of the owner's wealth, social status, and
hospitality
. The grandeur of the dining room was a way for the Romans to impress their guests and showcase their power and influence. The lavish
feasts
and
entertainment
in the dining room were a way for the owner to solidify their social connections and gain political favor.
In conclusion, the dining room in ancient Rome homes was more than just a place to eat. It was a reflection of the owner's wealth, a space for socializing and displaying their opulence, and a symbol of hospitality and power. The meticulous design and decoration of the dining room were a testament to the ancient Romans' love for grandeur and their desire to impress.
The dining room in ancient Rome homes was not just a mere functional space, but it also held symbolic significance. It was a representation of the owner's wealth, social status, and
hospitality
. The grandeur of the dining room was a way for the Romans to impress their guests and showcase their power and influence. The lavish
feasts
and
entertainment
in the dining room were a way for the owner to solidify their social connections and gain political favor.
In conclusion, the dining room in ancient Rome homes was more than just a place to eat. It was a reflection of the owner's wealth, a space for socializing and displaying their opulence, and a symbol of hospitality and power. The meticulous design and decoration of the dining room were a testament to the ancient Romans' love for grandeur and their desire to impress.