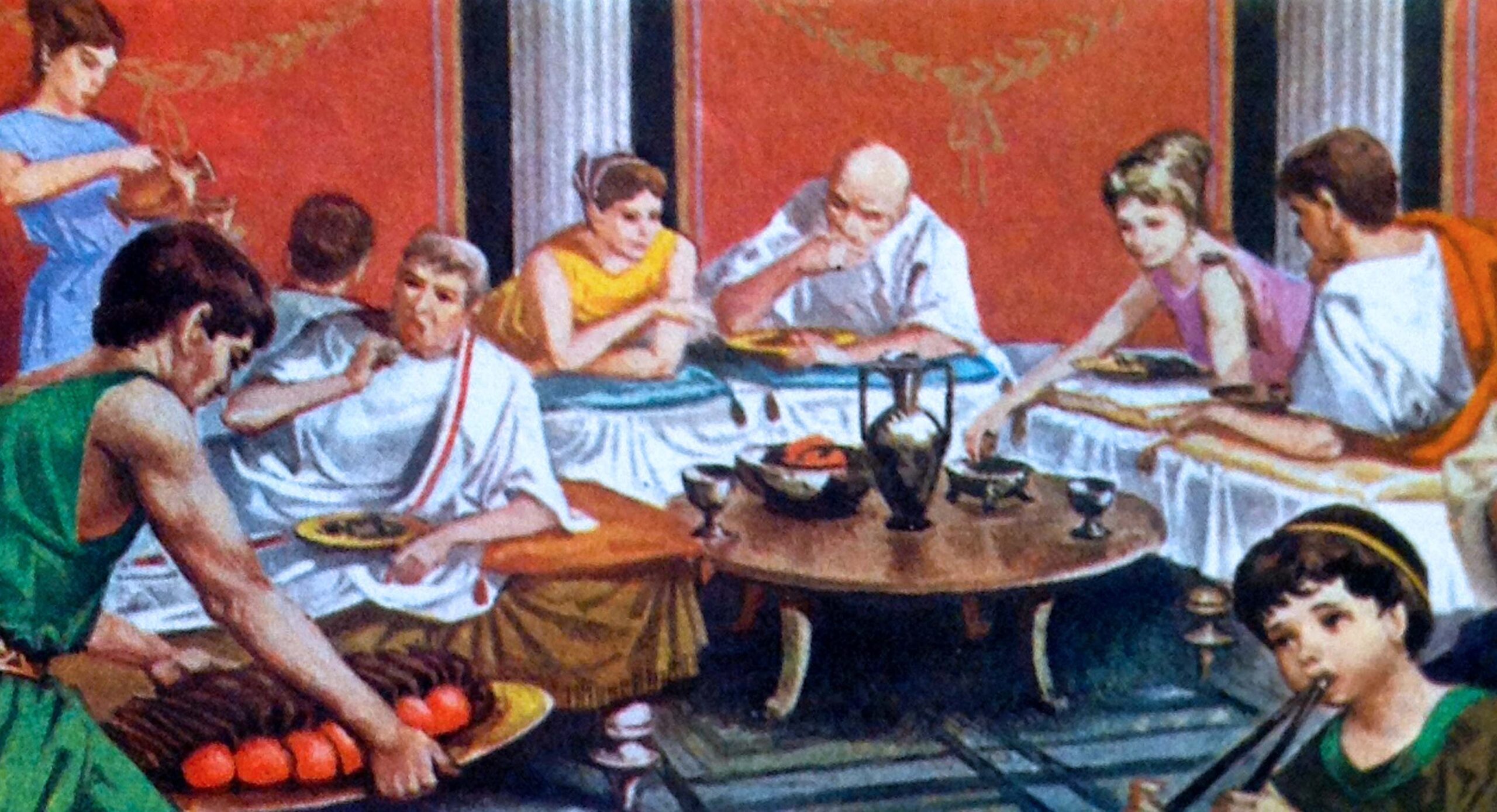
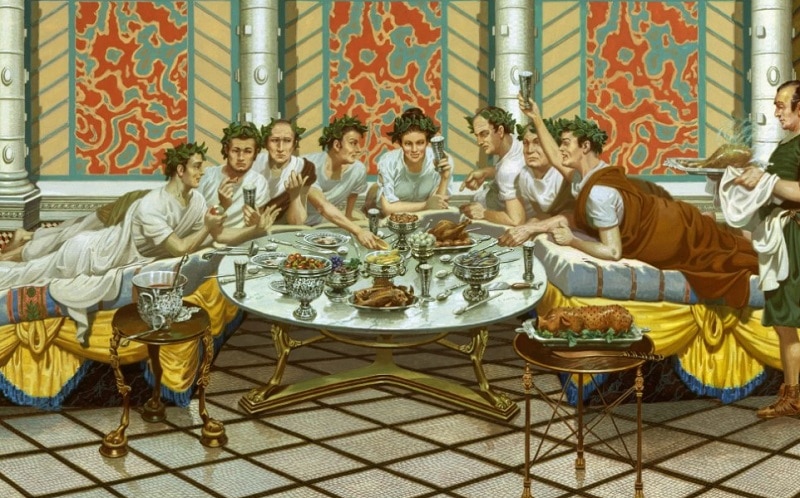
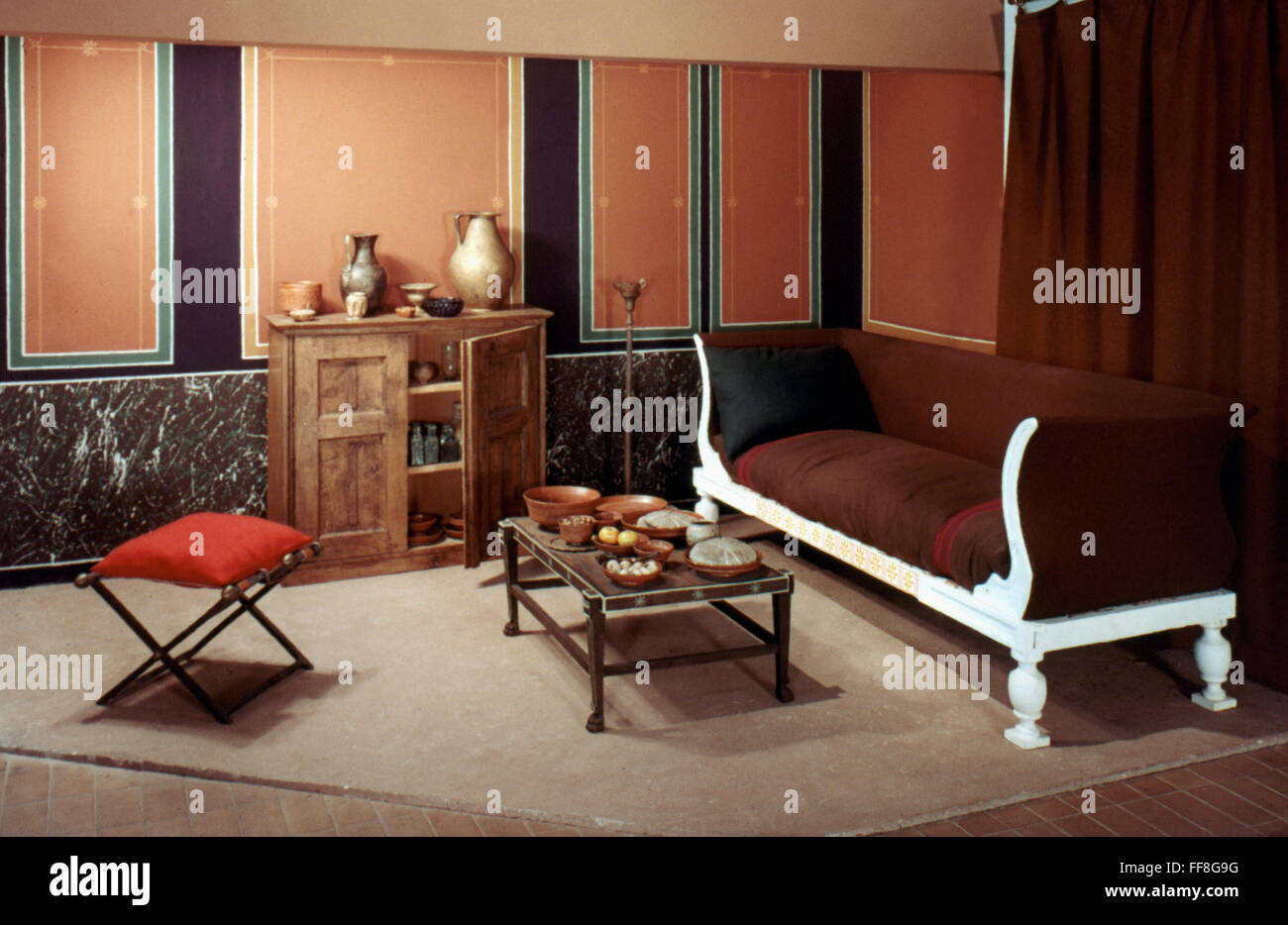
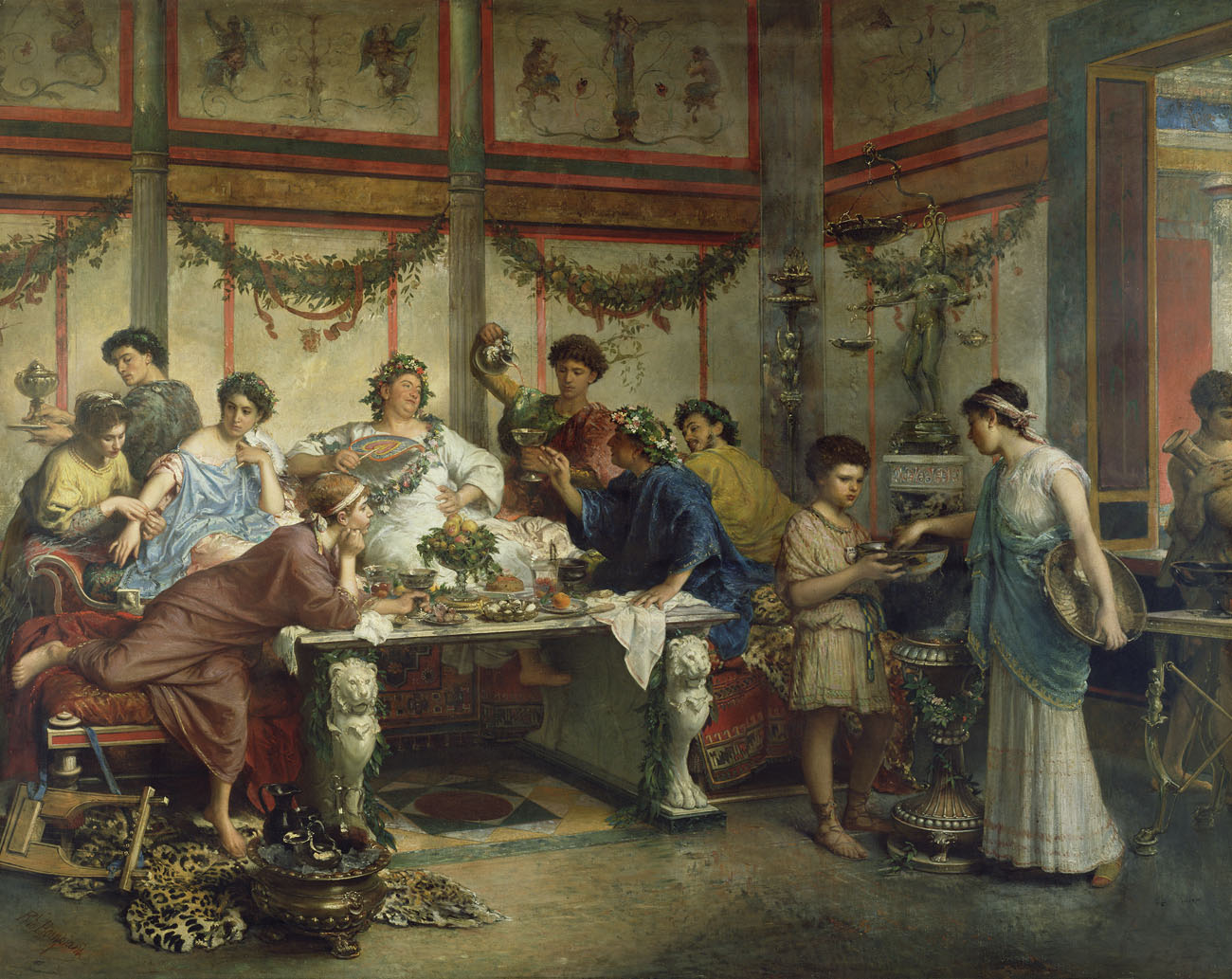
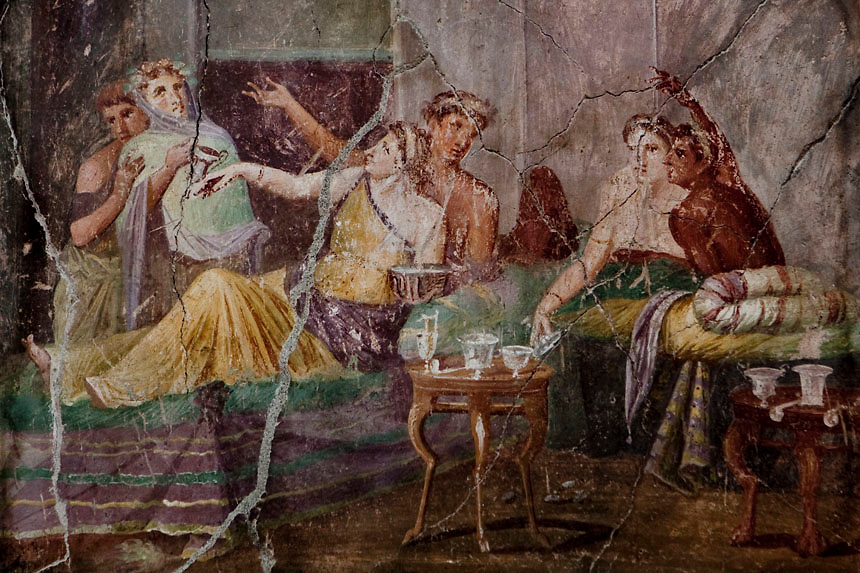The ancient Roman dining room, also known as the triclinium, was an integral part of Roman culture and society. It was a place where people gathered not just to eat, but also to socialize, discuss politics, and conduct business. The dining room was a reflection of the Roman lifestyle, with its lavish decorations and luxurious furnishings. Let's take a closer look at the top 10 features of the ancient Roman dining room. Ancient Roman Dining Room
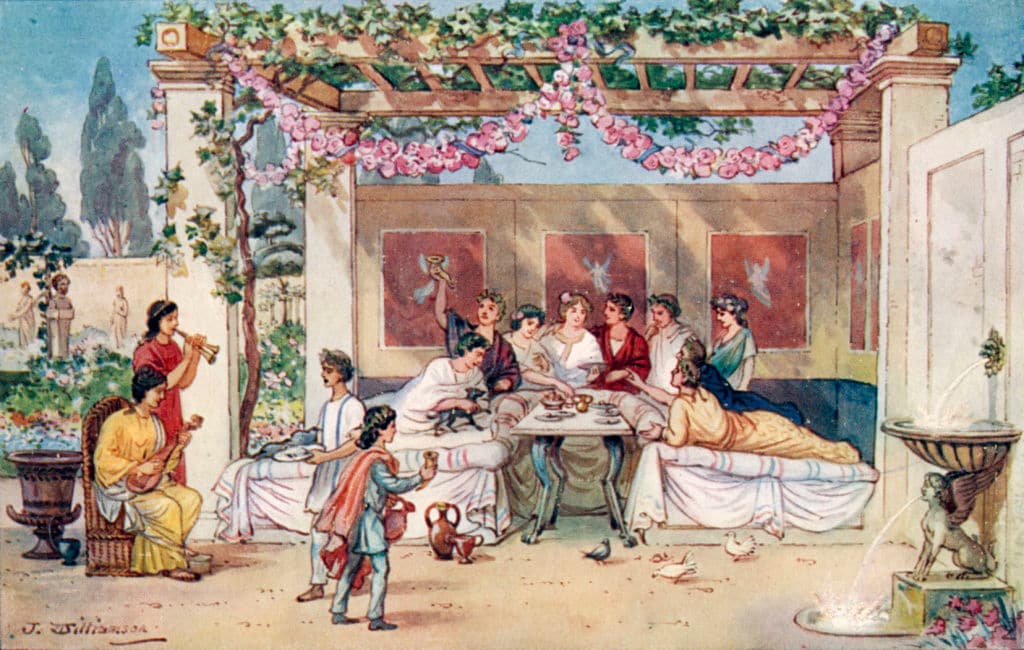
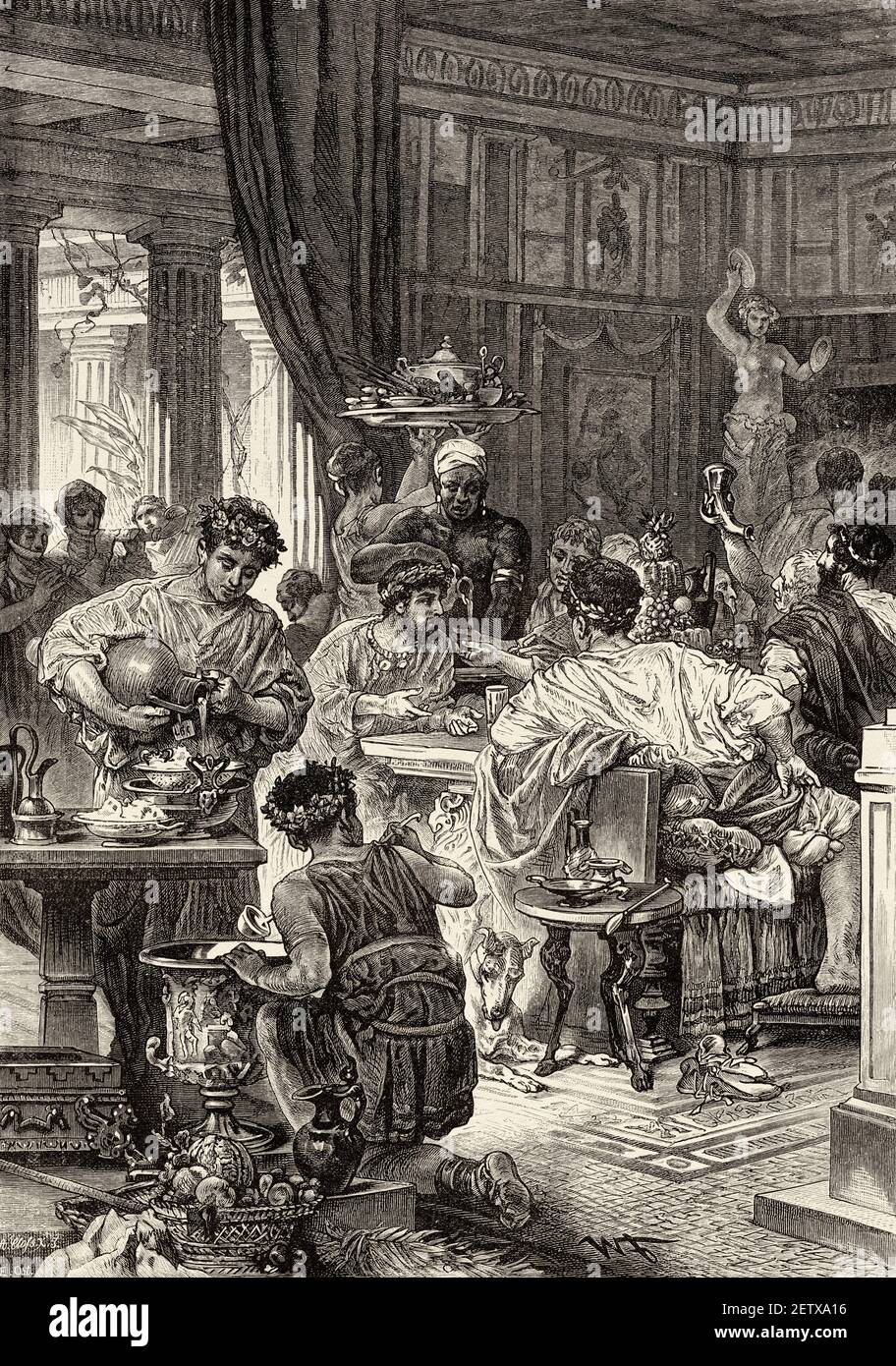
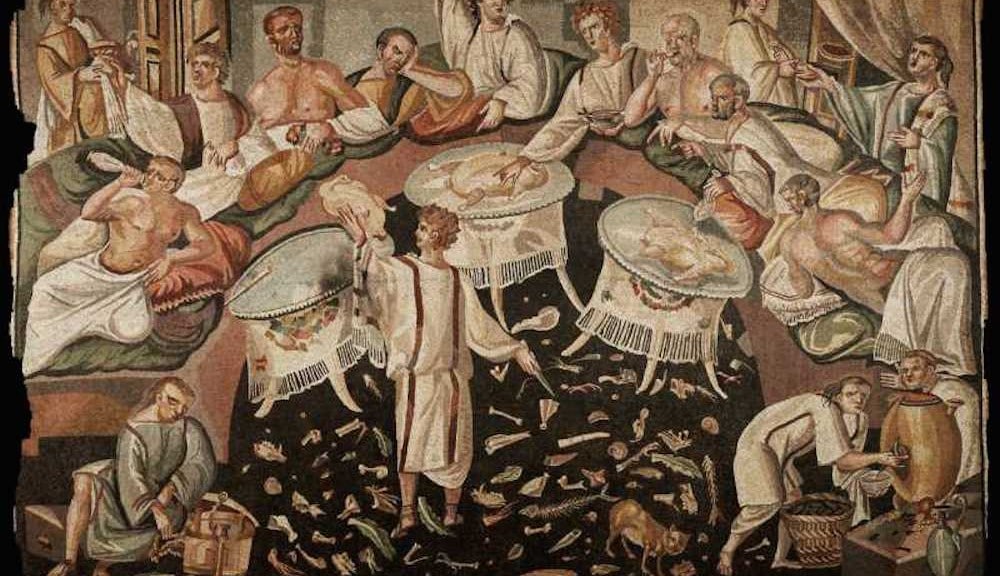
The convivium, or banquet, was a common occurrence in ancient Roman dining rooms. These lavish feasts were held for special occasions such as birthdays, weddings, and victory celebrations. The banquet was a display of wealth and social status, with rich, exotic foods and expensive wines being served. It was also a time for entertainment, with musicians, dancers, and acrobats performing for the guests. Ancient Roman Banquet
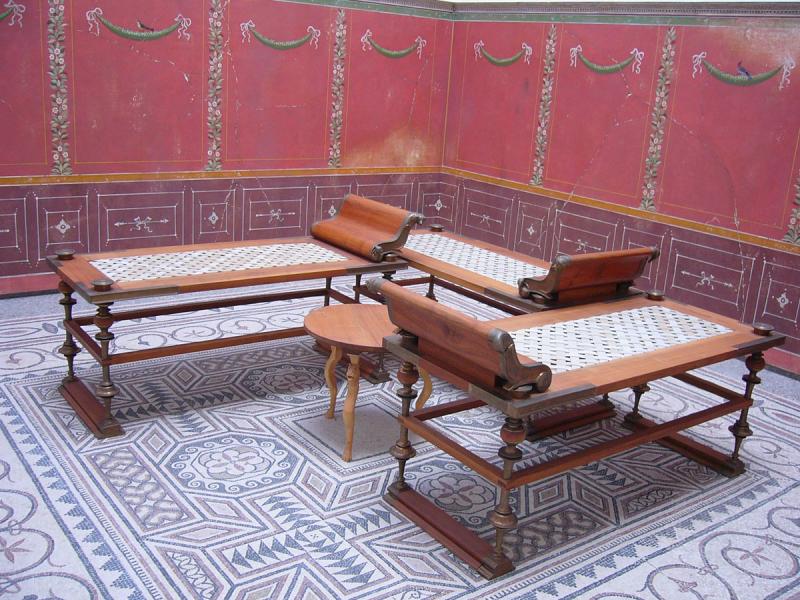
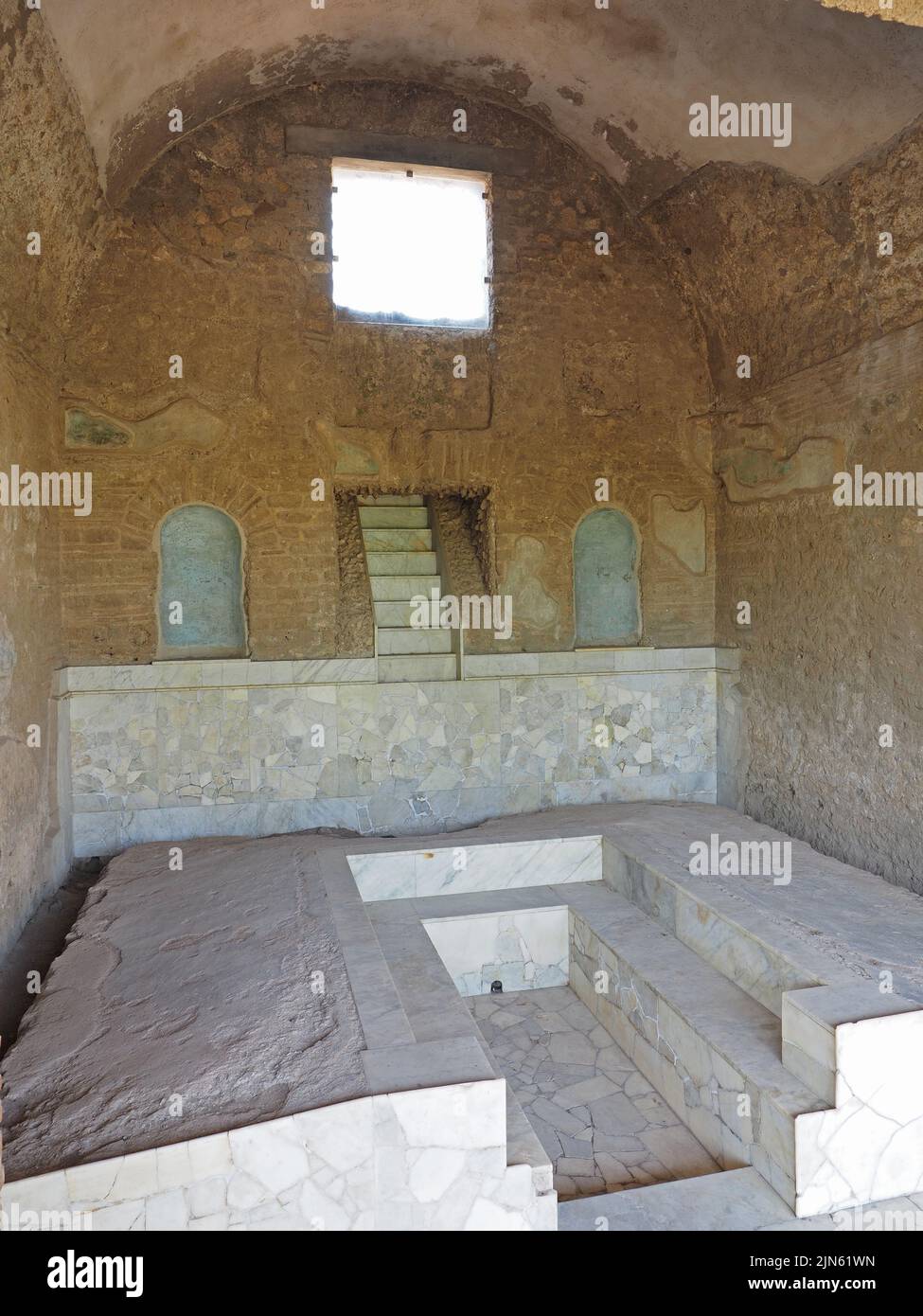
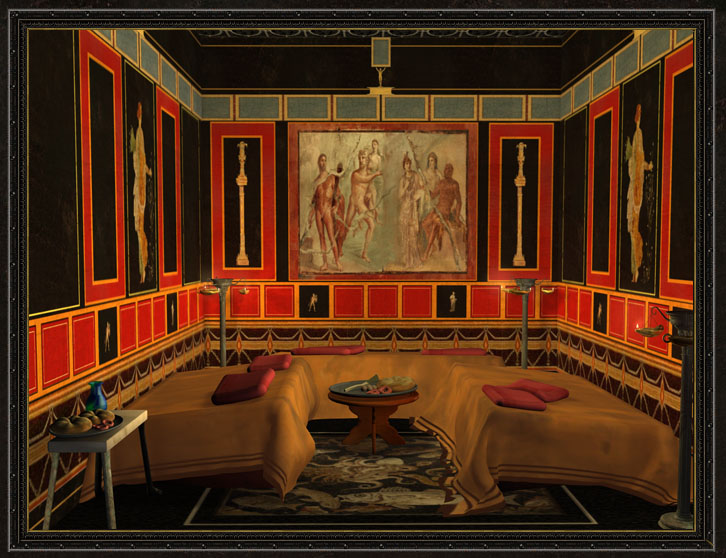
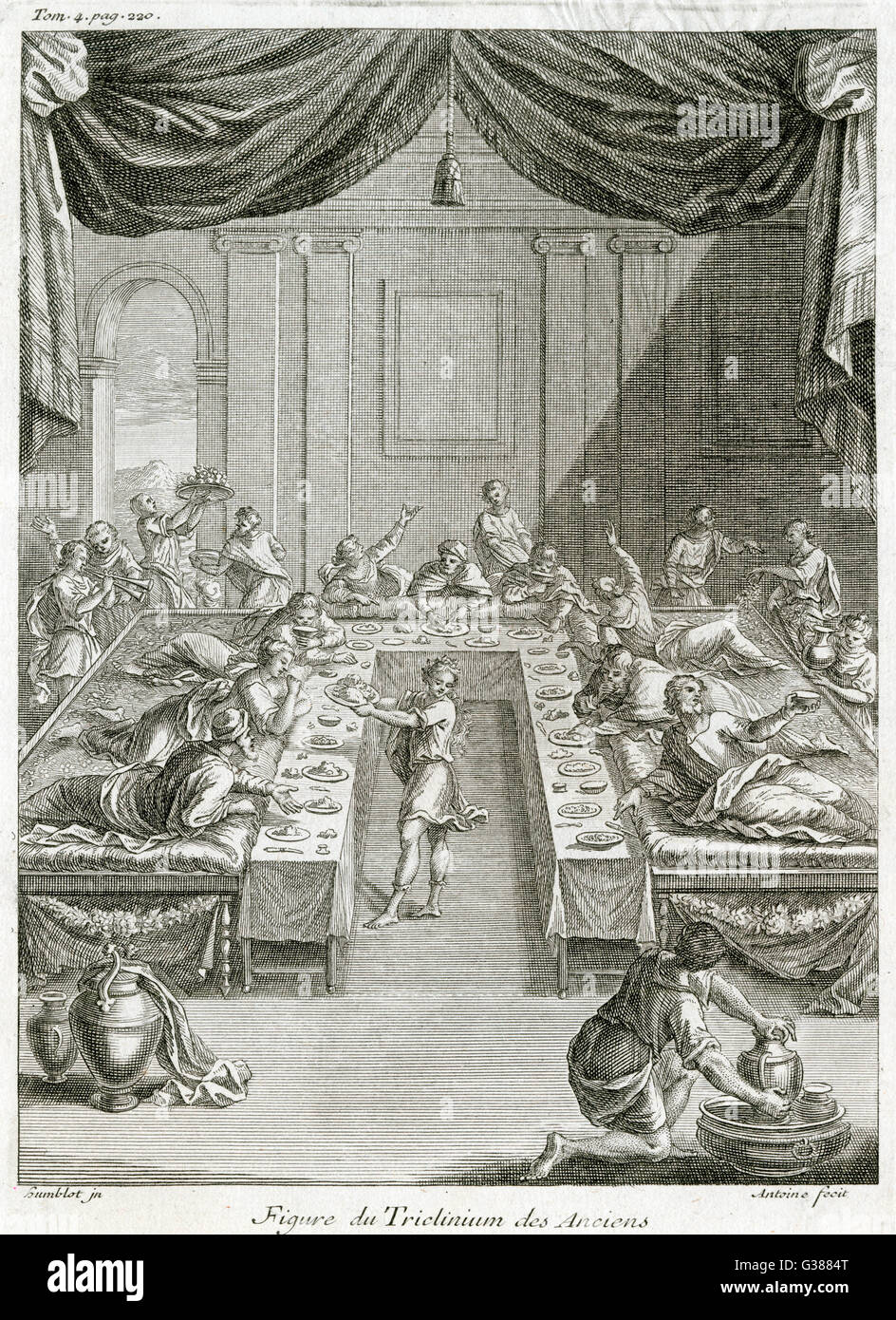
The triclinium was the formal dining room in a Roman house. It was typically located on the ground floor, near the atrium, and was the most elaborately decorated room in the house. The triclinium was designed for dining while reclining on triclinium couches, with three couches arranged around a central table. This setup symbolized the Roman practice of dining as a social event, rather than just for sustenance. Roman Triclinium
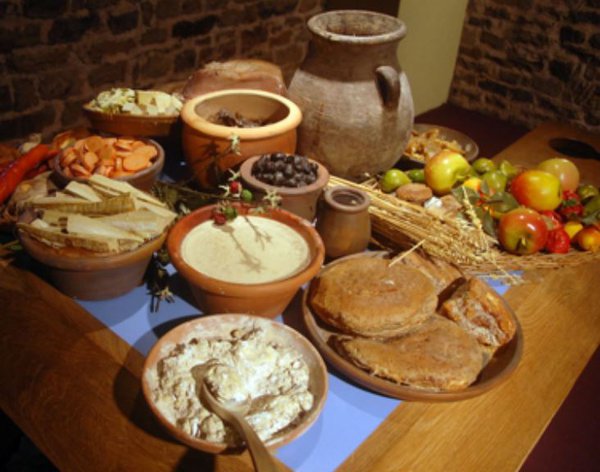
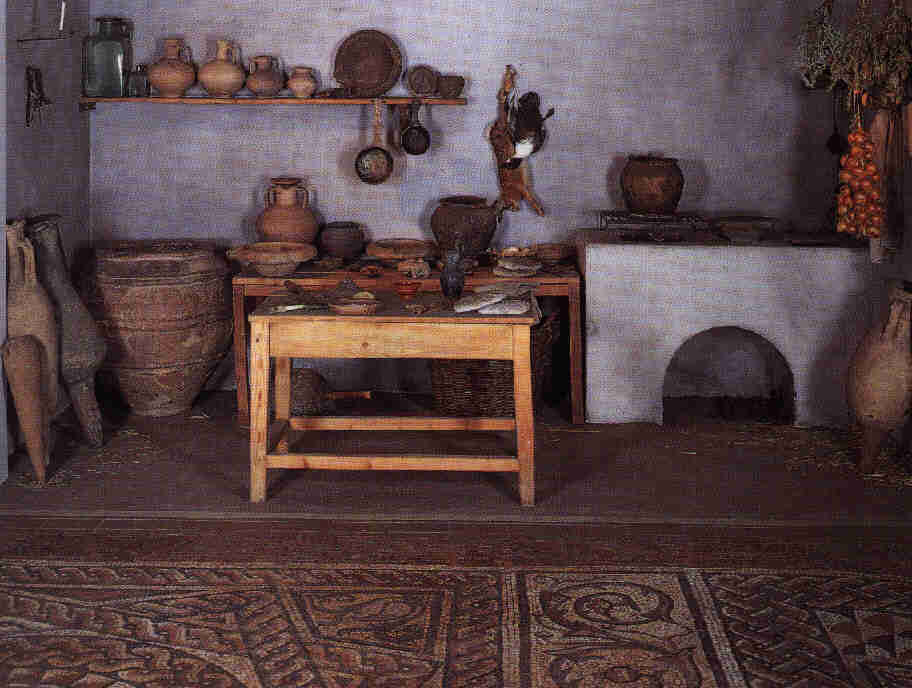
The culina, or kitchen, was an important part of the Roman dining room. It was where the meals were prepared and cooked, and it also served as a gathering place for the household. The kitchen was equipped with various tools and appliances for cooking, such as ovens, grills, and pots. It was also a place for slaves and servants to work, as the Romans believed that cooking was beneath the social status of the elite. Roman Culina
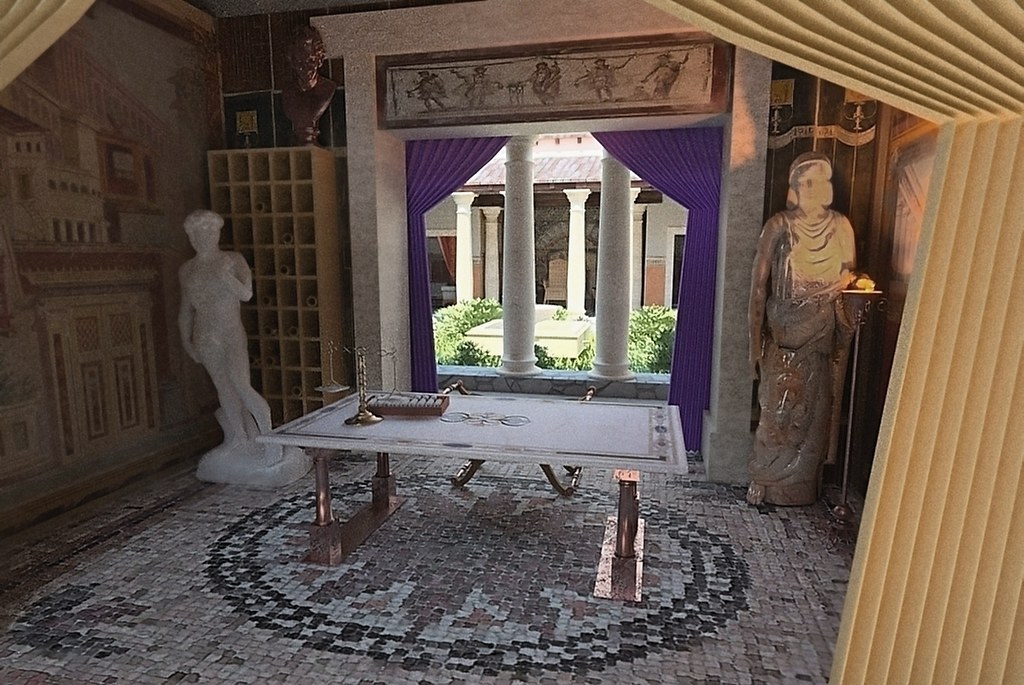
The atrium was the central courtyard of a Roman house, and it played a significant role in the dining room. It was the main entrance to the house and was often used as a reception area for guests. The atrium was also where the impluvium, a shallow pool used for collecting rainwater, was located. This pool not only provided a source of water for the household but also served as a decorative feature. Roman Atrium
The tablinum was a room connected to the atrium and served as a private office for the head of the household. It was also used as a display room for family portraits and other important artifacts. During banquets, the tablinum would be used as a dining room for the most important guests, as it was considered the most prestigious room in the house. Roman Tablinum
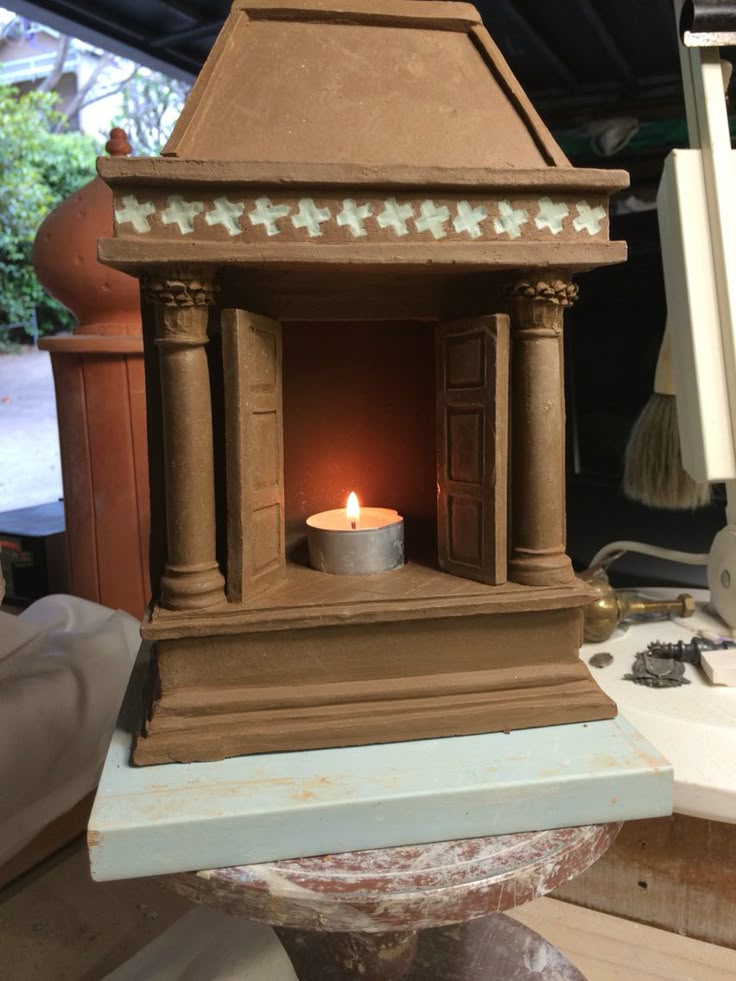
The lararium was a small shrine located in the atrium or peristylium (back garden) of a Roman house. It was dedicated to the household gods, known as the lares, and was an important part of daily life. The Romans would make offerings and prayers at the lararium before meals, as they believed the gods would protect and bless their food. Roman Lararium
The impluvium was a shallow pool located in the atrium of a Roman house, as mentioned earlier. It was an essential feature of the dining room, not just for its practical use but also for its aesthetic appeal. The impluvium was often decorated with intricate mosaics or frescoes, adding to the overall grandeur of the dining room. Roman Impluvium
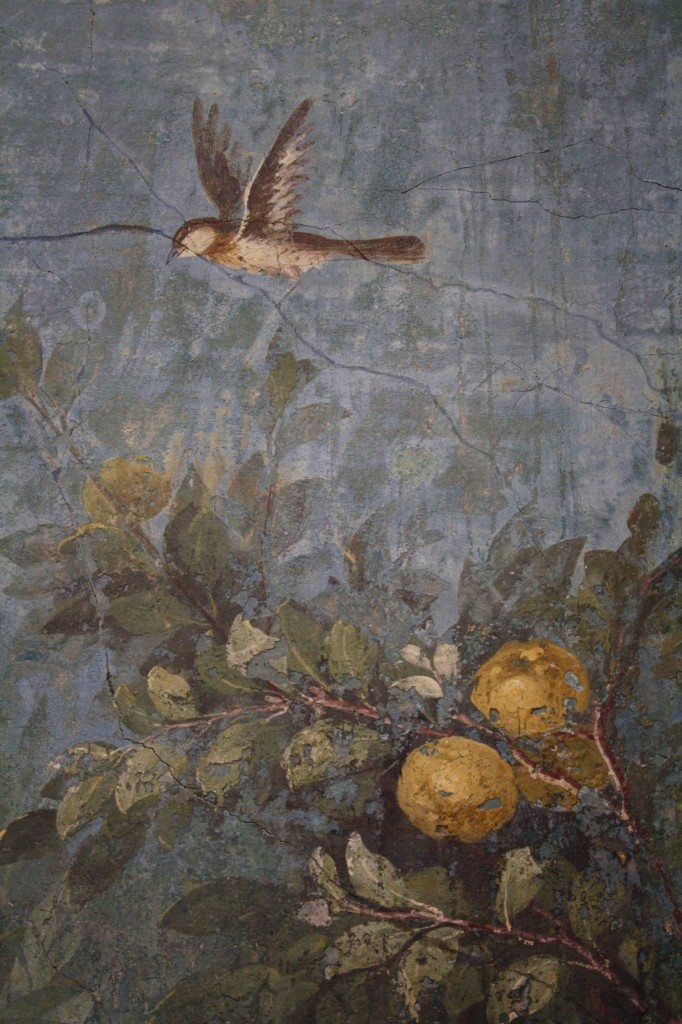
The walls of the triclinium were often adorned with colorful frescoes, depicting scenes from daily life, mythology, and nature. These frescoes were not only a form of decoration but also served as a conversation starter during meals. The most common themes found in triclinium frescoes were food, wine, and the gods. Roman Triclinium Fresco
Dining in ancient Rome was not just about eating; it was also about following strict social etiquette. Guests were expected to wash their hands before the meal, and food was eaten with the fingers or a small knife. The most important guest would be seated on the middle couch, with the host on the left and the second most important guest on the right. Conversation was encouraged during the meal, but it was considered impolite to talk with your mouth full. In conclusion, the ancient Roman dining room was much more than just a place to eat. It was a symbol of wealth, power, and social status, and it played a significant role in the daily lives of the Romans. The features and customs of the Roman dining room have left a lasting influence on modern dining culture, making it an important part of our history. Roman Dining Etiquette
The Importance of the Ancient Roman Dining Room in House Design

Creating a Space for Socialization and Entertainment
 The dining room has been a central part of house design for centuries, serving as a space for gathering, socializing, and enjoying meals together. However, the ancient Romans took this concept to a whole new level with their dining room design. In ancient Rome, the dining room, or "triclinium," was not only a place to eat but also a space for entertainment and socialization. This unique approach to house design has influenced modern-day dining room design in many ways.
A Place for Feasting and Entertainment
In ancient Rome, the dining room was not just a simple room with a table and chairs. It was a grand space, often adorned with beautiful frescoes and mosaics, to impress guests and show off one's wealth and status. The room was designed to accommodate large feasts, with couches or "lecti" arranged in a U-shape around a central table. This allowed for easy conversation and interaction among guests.
Music, poetry, and other forms of entertainment were also common during these feasts
, making the dining room a hub for socialization and enjoyment.
Influencing Modern Dining Room Design
The ancient Roman dining room has had a significant influence on modern-day house design, particularly when it comes to dining room design. The concept of having a separate space dedicated solely to dining and entertaining has remained a staple in house design. The use of couches or banquettes, instead of individual chairs, to create a more intimate and social dining experience is also a direct influence from ancient Roman design.
Creating a Sense of Luxury and Elegance
The ancient Romans were known for their love of luxury and opulence, and their dining room design was no exception. From the intricate frescoes on the walls to the elaborate feasts and entertainment, everything about the dining room exuded elegance and sophistication. This desire for luxury has also influenced modern-day dining room design, with many homeowners opting for grand and lavish dining spaces that reflect the opulence of ancient Rome.
In conclusion, the ancient Roman dining room was much more than just a functional space for eating. It was a place to socialize, entertain, and showcase one's wealth and status. Its influence on modern-day house design is evident in the continued importance of the dining room as a central gathering space and the incorporation of luxurious elements to create a sense of elegance.
The dining room has been a central part of house design for centuries, serving as a space for gathering, socializing, and enjoying meals together. However, the ancient Romans took this concept to a whole new level with their dining room design. In ancient Rome, the dining room, or "triclinium," was not only a place to eat but also a space for entertainment and socialization. This unique approach to house design has influenced modern-day dining room design in many ways.
A Place for Feasting and Entertainment
In ancient Rome, the dining room was not just a simple room with a table and chairs. It was a grand space, often adorned with beautiful frescoes and mosaics, to impress guests and show off one's wealth and status. The room was designed to accommodate large feasts, with couches or "lecti" arranged in a U-shape around a central table. This allowed for easy conversation and interaction among guests.
Music, poetry, and other forms of entertainment were also common during these feasts
, making the dining room a hub for socialization and enjoyment.
Influencing Modern Dining Room Design
The ancient Roman dining room has had a significant influence on modern-day house design, particularly when it comes to dining room design. The concept of having a separate space dedicated solely to dining and entertaining has remained a staple in house design. The use of couches or banquettes, instead of individual chairs, to create a more intimate and social dining experience is also a direct influence from ancient Roman design.
Creating a Sense of Luxury and Elegance
The ancient Romans were known for their love of luxury and opulence, and their dining room design was no exception. From the intricate frescoes on the walls to the elaborate feasts and entertainment, everything about the dining room exuded elegance and sophistication. This desire for luxury has also influenced modern-day dining room design, with many homeowners opting for grand and lavish dining spaces that reflect the opulence of ancient Rome.
In conclusion, the ancient Roman dining room was much more than just a functional space for eating. It was a place to socialize, entertain, and showcase one's wealth and status. Its influence on modern-day house design is evident in the continued importance of the dining room as a central gathering space and the incorporation of luxurious elements to create a sense of elegance.















































































.jpg)