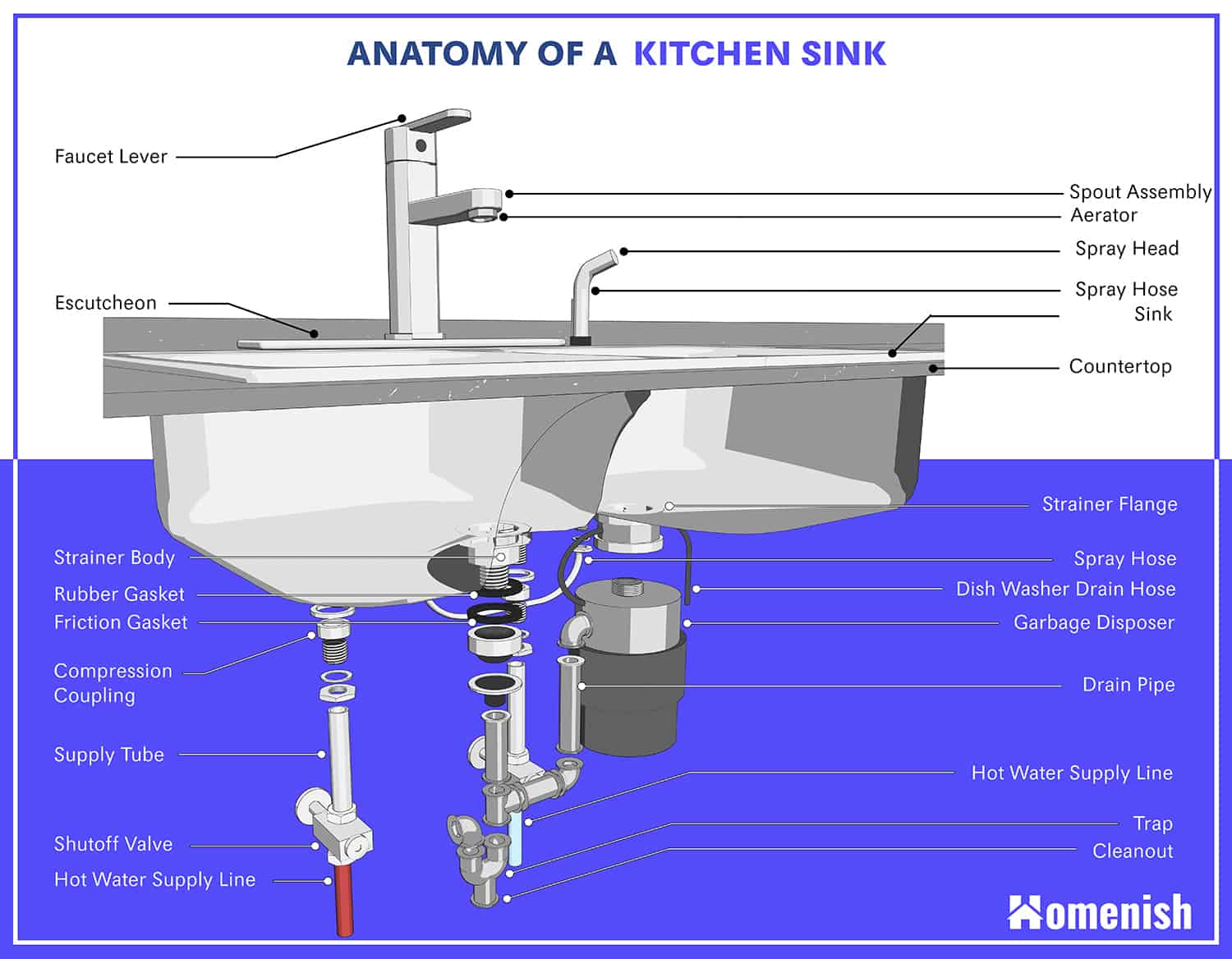
The Kitchen Sink Theory is a concept that describes the tendency of individuals to include all possible factors, even those that are irrelevant, when making a decision. This theory suggests that people have a natural inclination to consider every aspect of a situation, similar to how everything in a kitchen sink is thrown in to be cleaned. This can lead to decision-making processes that are inefficient and ineffective. For example, imagine you are trying to decide which car to purchase. According to the Kitchen Sink Theory, you may consider not only the make and model, but also factors such as color, gas mileage, safety ratings, and even the car's history. While some of these factors may be important, others may not necessarily affect your decision. This can make the decision-making process more complex and time-consuming.Kitchen Sink Theory: Definition and Examples
The Kitchen Sink Theory was first introduced by psychologist Roy F. Baumeister in the late 1980s. Baumeister conducted a series of experiments to test the theory and found that individuals tend to use more information than necessary when making decisions. This can lead to a phenomenon known as "decision paralysis," where individuals become overwhelmed by the amount of information and have difficulty making a choice. However, the Kitchen Sink Theory has also been criticized for oversimplifying the decision-making process and disregarding the importance of considering multiple factors. Some argue that including all possible information can actually lead to better decisions, as it allows for a more thorough evaluation of the situation.The Kitchen Sink Theory: A Comprehensive Guide
The Kitchen Sink Theory is based on the idea that humans have a natural desire for completeness and perfection. This drive can manifest in decision-making processes as individuals try to consider every possible factor to make the "perfect" choice. However, in reality, this can lead to a decision that is not necessarily the best one. For example, imagine you are planning a vacation and are looking at different destinations. According to the Kitchen Sink Theory, you may consider not only the cost, weather, and activities available, but also factors such as the political climate, cultural norms, and even the type of food available. While these factors may be interesting, they may not necessarily be relevant to your decision and can cause unnecessary stress and confusion.The Kitchen Sink Theory: What It Is and How It Works
The Kitchen Sink Theory is often used as a metaphor to describe the decision-making process. Just as everything in a kitchen sink is thrown in to be cleaned, individuals tend to include all possible factors when making a decision. This can lead to an overwhelming amount of information and ultimately, a less efficient decision-making process. However, it is important to note that the Kitchen Sink Theory is not a universal explanation for decision-making processes. Factors such as individual differences, personal biases, and external influences can also play a significant role in how people make decisions.The Kitchen Sink Theory: An Overview
When faced with a decision, individuals may experience a cognitive overload as they try to consider all possible factors. This can lead to feelings of stress, uncertainty, and difficulty in making a final decision. The Kitchen Sink Theory suggests that this is a result of our innate desire for completeness and perfection, and our tendency to overcomplicate the decision-making process. However, it is important to strike a balance between considering all relevant information and becoming overwhelmed by irrelevant details. This can be achieved by prioritizing and focusing on the most important factors, rather than trying to include every single one.The Kitchen Sink Theory: Explained
While the Kitchen Sink Theory has been widely accepted and used in various fields, it has also been met with criticism. Some argue that it oversimplifies the decision-making process and disregards the importance of considering multiple factors. Others argue that including all possible information can actually lead to better decisions, as it allows for a more comprehensive evaluation of the situation. Furthermore, the Kitchen Sink Theory has been criticized for its lack of consideration for individual differences and external influences. Each person may have their own unique decision-making style and may be influenced by factors such as their upbringing, culture, and personal biases.The Kitchen Sink Theory: A Critical Analysis
The Kitchen Sink Theory was first introduced by psychologist Roy F. Baumeister in the late 1980s. Since then, it has been studied and applied in various fields, including psychology, economics, and marketing. Over time, the theory has evolved and been refined to better explain the decision-making process. Some researchers have expanded on the Kitchen Sink Theory by introducing the concept of "information overload," which suggests that too much information can lead to a decrease in the quality of decision-making. Others have proposed alternative theories, such as the "garbage can model," which suggests that decisions are made based on a combination of random factors and available solutions.The Kitchen Sink Theory: Origins and Evolution
The Kitchen Sink Theory has been widely studied and applied in the field of psychology. It has been used to explain various decision-making processes, from everyday choices to more complex ones. The theory has also been used to understand how individuals cope with information overload and how different decision-making styles can affect the outcome of a decision. Furthermore, the Kitchen Sink Theory has been used in therapeutic settings to help individuals make more efficient and effective decisions. By understanding the tendency to include all possible factors, individuals can learn to prioritize and focus on the most relevant information, leading to better decision-making outcomes.The Kitchen Sink Theory: Applications in Psychology
While the Kitchen Sink Theory has been widely accepted and used in various fields, it is not without its limitations. As mentioned earlier, the theory has been criticized for oversimplifying the decision-making process and disregarding the importance of considering multiple factors. Additionally, the Kitchen Sink Theory may not apply to all decision-making situations. Some decisions may require a more thorough evaluation of all possible factors, while others may only require a few key considerations. It is important to consider the context and individual differences when applying this theory.The Kitchen Sink Theory: Criticisms and Limitations
The Kitchen Sink Theory has important implications for decision-making processes in various fields. By understanding the tendency to include all possible factors, individuals can learn to prioritize and focus on the most relevant information, leading to more efficient and effective decision-making outcomes. For example, in business settings, understanding the Kitchen Sink Theory can help organizations streamline their decision-making processes and avoid information overload. In personal decision-making, individuals can use this knowledge to make more efficient choices and avoid becoming overwhelmed by irrelevant factors.The Kitchen Sink Theory: Implications for Decision Making
Kitchen Sink Meaning Theory: A Key Element in House Design

The Importance of House Design
 House design is an essential aspect of creating a comfortable and functional living space. It involves carefully considering the layout, materials, and overall aesthetic of a house to ensure that it meets the needs and preferences of its inhabitants. A well-designed house not only provides a sense of comfort and security but also reflects the personality and style of its owner. With the ever-changing trends in interior design, it can be challenging to keep up with the latest concepts and theories. However, one theory that has stood the test of time and has become a staple in house design is the kitchen sink meaning theory.
House design is an essential aspect of creating a comfortable and functional living space. It involves carefully considering the layout, materials, and overall aesthetic of a house to ensure that it meets the needs and preferences of its inhabitants. A well-designed house not only provides a sense of comfort and security but also reflects the personality and style of its owner. With the ever-changing trends in interior design, it can be challenging to keep up with the latest concepts and theories. However, one theory that has stood the test of time and has become a staple in house design is the kitchen sink meaning theory.
Understanding the Kitchen Sink Meaning Theory
 The kitchen sink meaning theory is a concept that emphasizes the importance of the kitchen sink as the focal point of a house. It suggests that the placement, design, and functionality of the kitchen sink can significantly impact the overall look and feel of a house. This theory originated from the idea that the kitchen is the heart of a home, and the sink is the heart of the kitchen. It is where most of the food preparation, cooking, and cleaning takes place, making it a vital element in daily household activities.
According to this theory, the kitchen sink has a symbolic meaning that goes beyond its practical purpose.
It represents the flow of energy and resources in a household, as well as the flow of emotions and relationships within a family. Therefore, the placement and design of the kitchen sink should be carefully considered to promote positive energy and harmony in the household.
The kitchen sink meaning theory is a concept that emphasizes the importance of the kitchen sink as the focal point of a house. It suggests that the placement, design, and functionality of the kitchen sink can significantly impact the overall look and feel of a house. This theory originated from the idea that the kitchen is the heart of a home, and the sink is the heart of the kitchen. It is where most of the food preparation, cooking, and cleaning takes place, making it a vital element in daily household activities.
According to this theory, the kitchen sink has a symbolic meaning that goes beyond its practical purpose.
It represents the flow of energy and resources in a household, as well as the flow of emotions and relationships within a family. Therefore, the placement and design of the kitchen sink should be carefully considered to promote positive energy and harmony in the household.
Applying the Kitchen Sink Meaning Theory in House Design
 There are several ways to incorporate the kitchen sink meaning theory into house design.
One way is to choose a sink that reflects the overall style and theme of the house.
For example, a farmhouse-style sink would be a perfect fit for a rustic-themed kitchen, while a sleek and modern sink would complement a contemporary kitchen.
Another important aspect is the placement of the sink.
It should be positioned in a way that allows the cook to face the entrance of the kitchen, which represents the flow of energy into the house.
In addition to the physical aspects, the functionality of the kitchen sink is also crucial in promoting positive energy in a household.
Having a well-designed sink that makes cooking and cleaning more efficient can reduce stress and improve the overall atmosphere of the house.
It is also essential to keep the sink area clutter-free and well-maintained to prevent any negative energy from accumulating.
In conclusion, the kitchen sink meaning theory is a key element in house design that should not be overlooked. By understanding and applying this theory, one can create a harmonious and functional living space that reflects their unique style and promotes positive energy in the household.
So the next time you design or renovate your house, make sure to give special attention to the kitchen sink - the heart of your home.
There are several ways to incorporate the kitchen sink meaning theory into house design.
One way is to choose a sink that reflects the overall style and theme of the house.
For example, a farmhouse-style sink would be a perfect fit for a rustic-themed kitchen, while a sleek and modern sink would complement a contemporary kitchen.
Another important aspect is the placement of the sink.
It should be positioned in a way that allows the cook to face the entrance of the kitchen, which represents the flow of energy into the house.
In addition to the physical aspects, the functionality of the kitchen sink is also crucial in promoting positive energy in a household.
Having a well-designed sink that makes cooking and cleaning more efficient can reduce stress and improve the overall atmosphere of the house.
It is also essential to keep the sink area clutter-free and well-maintained to prevent any negative energy from accumulating.
In conclusion, the kitchen sink meaning theory is a key element in house design that should not be overlooked. By understanding and applying this theory, one can create a harmonious and functional living space that reflects their unique style and promotes positive energy in the household.
So the next time you design or renovate your house, make sure to give special attention to the kitchen sink - the heart of your home.